5 Common Mistakes in Industrial Steam Distribution Systems
Are you confident your industrial steam distribution system is operating efficiently? Or might it contain hidden errors that silently drain hundreds of millions in production costs? In this article, we unveil five technical pitfalls, distilled from over a decade of hands-on experience in industrial plants—and include proven solutions endorsed by USAID.
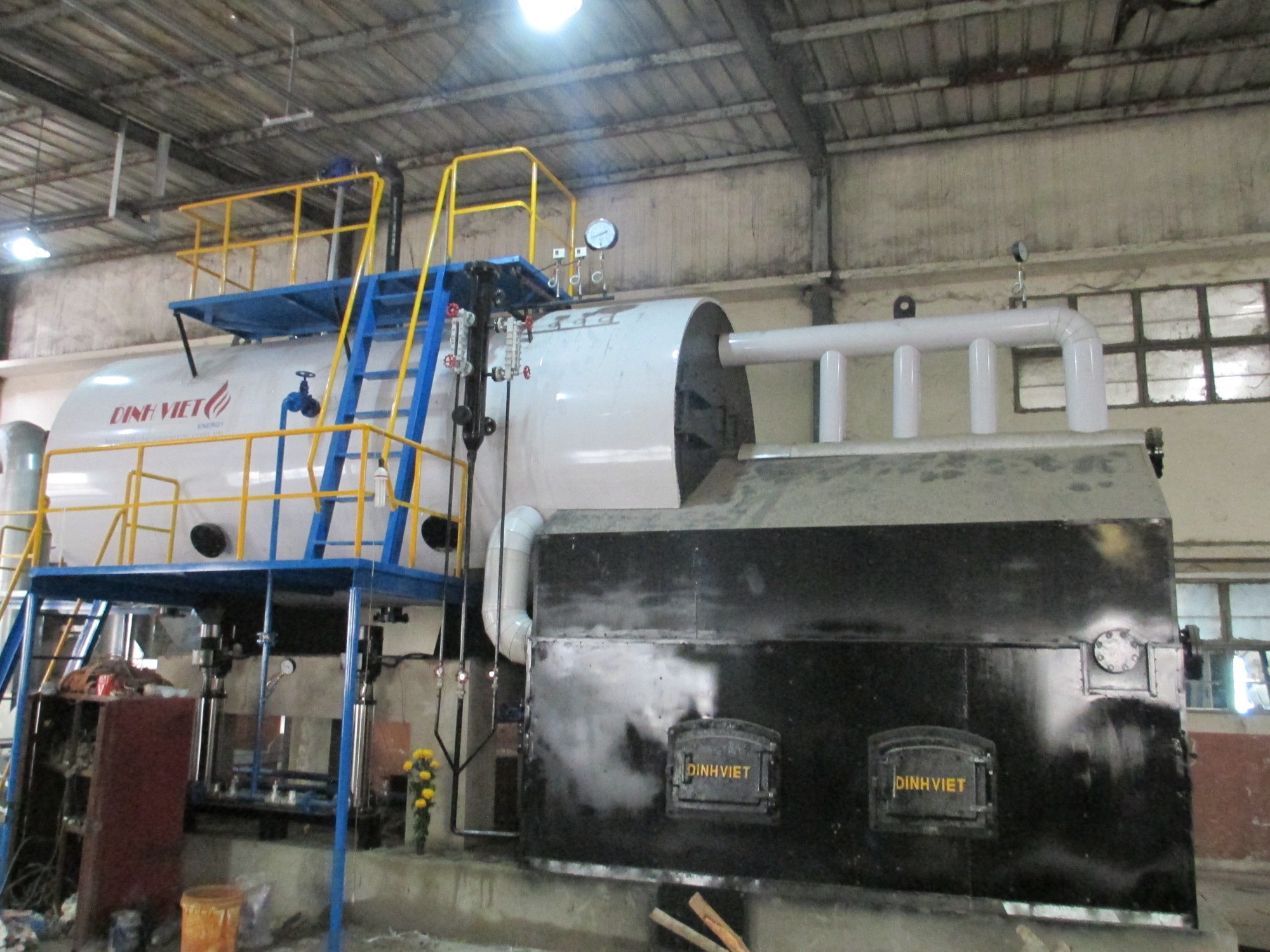
1. Overview of Industrial Steam Distribution Systems
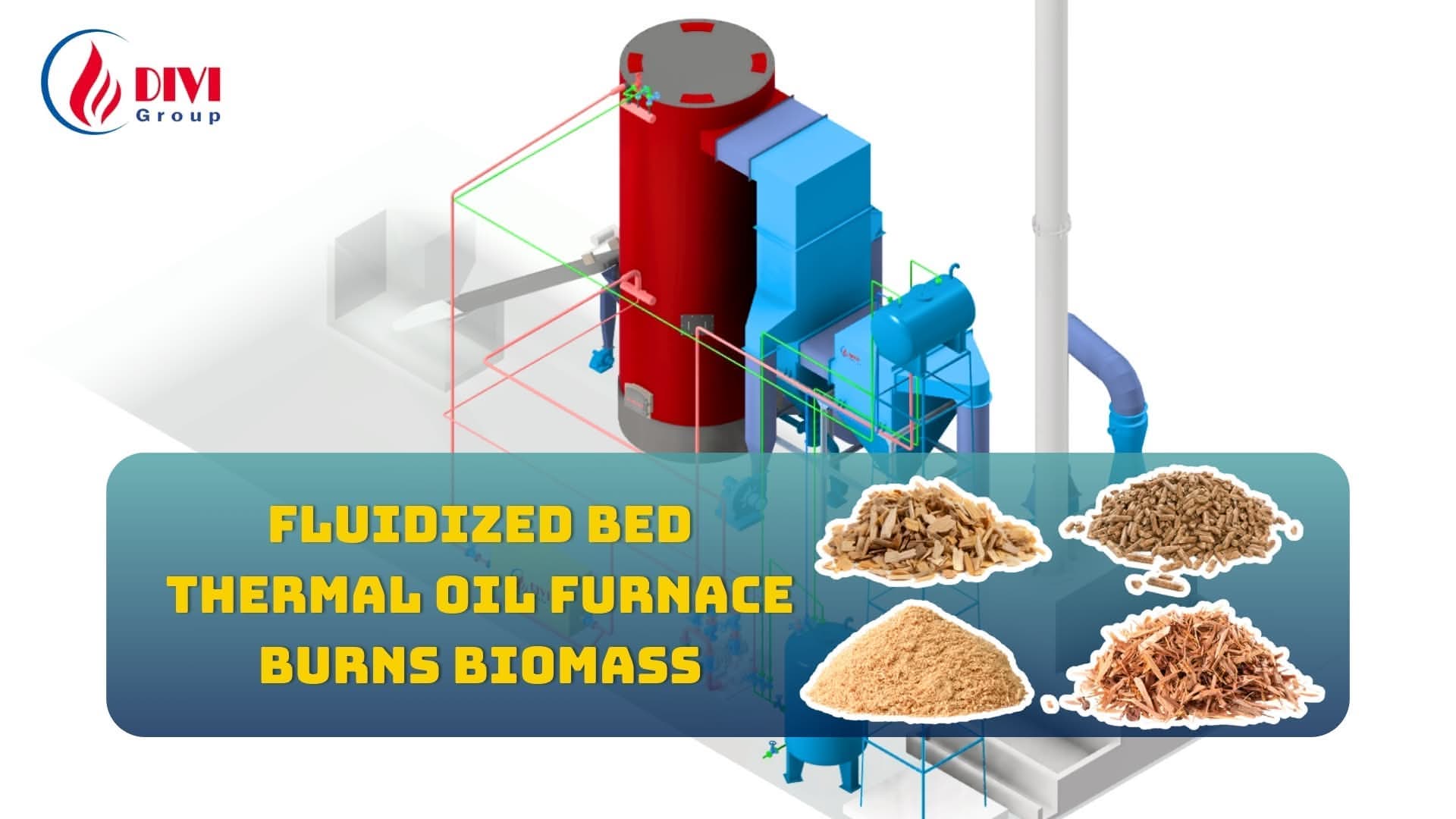
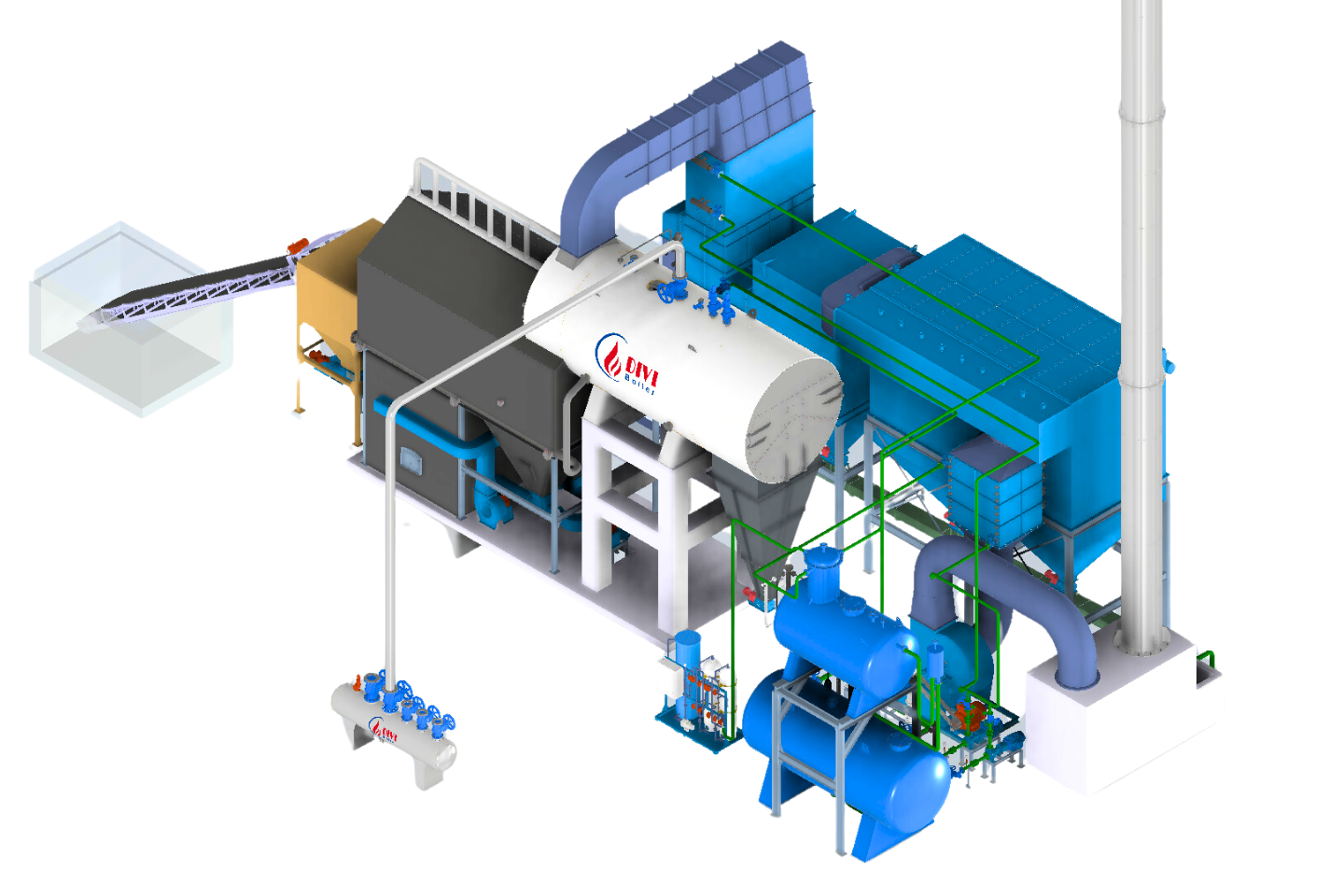
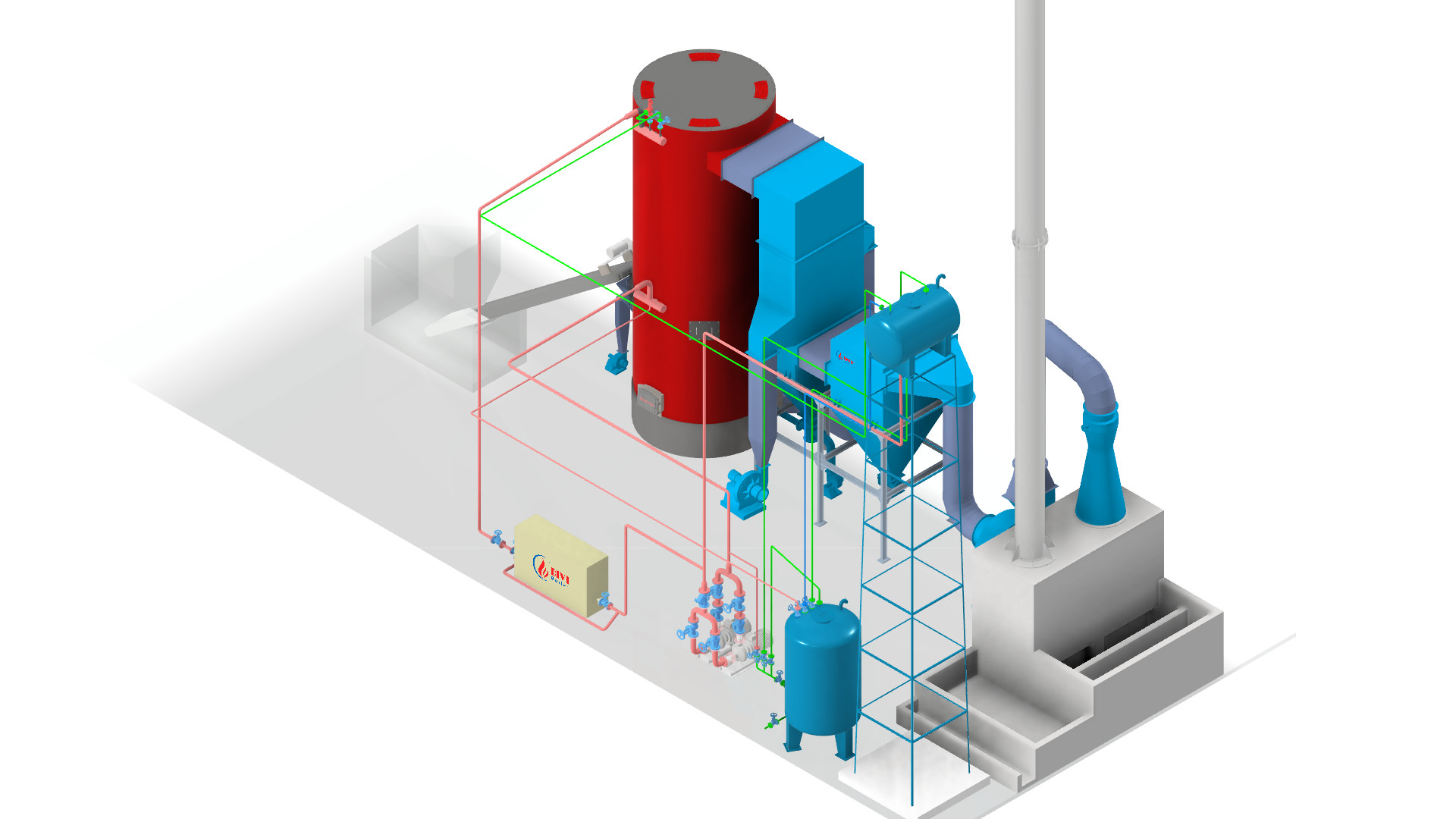
 Typical Steam Distribution System
Typical Steam Distribution SystemIndustrial steam distribution systems are engineered networks designed to transport saturated steam from the boiler to end-use equipment such as presses, dryers, or industrial heaters. These systems typically include critical components like steam piping, steam traps, pressure-reducing valves, check valves, and condensate return units.
To achieve optimal performance, industrial steam distribution systems must ensure that steam remains consistently dry, at the correct pressure and temperature. Maintaining these conditions is essential for efficient heat transfer, improved energy utilization, and significant fuel savings.
A well-designed and properly maintained steam distribution system directly contributes to operational safety, energy efficiency, and overall production reliability in industrial environments.
The key components of industrial steam distribution systems include:
-
Main and branch steam pipes: Deliver steam from the boiler to the point of use.
-
Steam traps: Remove condensate from the system while retaining dry steam.
-
Pressure reducing valves and safety valves: Regulate pressure to protect equipment.
-
Condensate recovery equipment: Returns hot condensate to the boiler for heat reuse.
Proper design and operation of an industrial steam distribution system not only stabilizes the production process but also significantly reduces energy costs, extends equipment lifespan, and ensures compliance with industrial energy efficiency standards.
Why the Steam Distribution System Affects Operational Costs
An efficient steam distribution system not only ensures steam quality but also deeply affects a plant’s energy expenses. When steam remains dry, heat transfer efficiency at user equipment improves, leading to significant fuel savings.
However, if condensate enters the steam due to design or operational errors, it results in:
-
Reduced heat transfer efficiency,
-
Longer heating times and excessive fuel use,
-
Hidden losses in productivity and product quality.
Even a single small fault—such as a malfunctioning steam trap or an incorrectly placed steam take-off—can cost businesses tens of tons of fuel per year.
Thus, investing in correct design, regular inspections, and maintenance of the steam system is crucial to control expenses and ensure reliable production.
5 Common Mistakes & Solutions in Steam Distribution
A poorly designed or maintained industrial steam distribution system can lead to severe energy losses, unstable operations, and soaring fuel costs. Below are five critical mistakes commonly found in factories — along with practical solutions that help cut waste and improve system reliability.
1. Incorrect Steam Take-Off Location
 Correct steam extraction point
Correct steam extraction pointSymptoms & Consequences
-
Steam is extracted from the bottom of the main pipe.
-
Condensate enters downstream equipment.
-
Leads to reduced heat transfer and issues like fabric discoloration in the textile industry.
Solution
-
Move the steam take-off point to the pipe crown to extract only dry steam.
-
Install a steam trap at each branch to prevent condensate intrusion.
2. Low-Quality or Faulty Steam Traps
 Types of high-quality steam traps
Types of high-quality steam trapsSymptoms & Consequences
-
Faulty traps release both steam and condensate.
-
Causes live steam to escape before heat transfer, resulting in fuel loss.
Solution
-
Use high-efficiency steam traps with proven performance in industrial conditions.
-
Case Study: DIVI Group achieved full return on investment within 3–6 months by upgrading traps in their industrial steam distribution system.
3. Returning Condensate to an Open Tank
Symptoms & Consequences
-
Hot condensate (~4 bar / 150°C) is dumped into an atmospheric tank (100°C).
-
Causes flash steam and significant thermal energy loss.
Solution
-
Maintain condensate pressure and pump it directly back to the boiler.
-
Outcome: Up to 30% fuel savings across the entire steam distribution network.
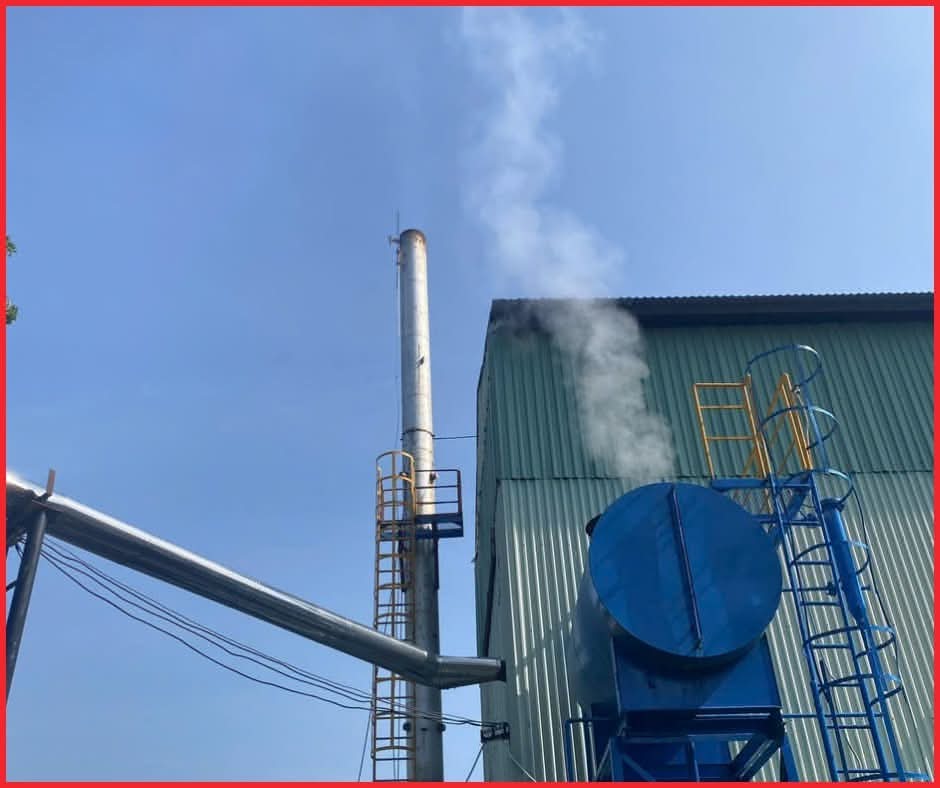 Steam escapes from the open water tank
Steam escapes from the open water tank4. Missing Check Valves
Symptoms & Consequences
-
Without check valves, condensate from one machine can flow back into another.
-
Results in temperature instability and unreliable production cycles.
Solution
-
Install check valves downstream of each steam trap to enforce one-way flow.
 A check valve should be installed
A check valve should be installed5. Lack of Insulation on Piping
Symptoms & Consequences
-
Uninsulated pipes and flanges release radiant heat.
-
Example: A Φ114 pipe without insulation wastes 0.34 kg of wood fuel/hour/meter → up to 22 tons/year per 100 meters.
Solution
-
Apply industrial-grade pipe insulation throughout the system.
-
Use insulated jackets for flanges and valves to minimize thermal loss.
By identifying and addressing these five issues, you can dramatically improve the efficiency of your industrial steam distribution systems, reduce fuel consumption, and extend the life of your process equipment.
Case Study: $100,000 USAID Grant Awarded for Steam Distribution Optimization
In many manufacturing plants—particularly in the textile, food processing, and chemical industries—condensate return is still done through open tanks or without proper pressure control. This outdated practice leads to major thermal energy losses, driving up fuel consumption and operational costs.
To solve this issue, DIVI Group implemented an optimized solution focusing on direct high-pressure condensate return in industrial steam distribution systems.
 USAID Grant of USD 100,000
USAID Grant of USD 100,000
1. Optimization Strategy & Results
DIVI Group upgraded its industrial steam distribution system by implementing the following measures:
-
Eliminated intermediate open tanks to avoid energy loss from depressurized condensate.
-
Installed high-pressure condensate return pumps to maintain temperature around 150°C, instead of letting it drop to 100°C.
-
Synchronized the entire system with steam traps, pressure-reducing valves, and digital controllers to stabilize both flow rate and pressure.
Key outcomes:
-
30% reduction in steam fuel consumption.
-
Payback period of just 5 months.
-
The solution was awarded a $100,000 grant from USAID in recognition of its practical contribution to industrial energy efficiency.
2. Real-World Applications & Final Insights
The optimized solution has been successfully applied in various industries:
-
Textile sector: Steam spraying, ironing, and thermal pressing.
-
Food industry: Heating for autoclaves, cooking tanks, and distillation systems.
-
Chemical plants: Heat exchangers and high-temperature reaction chambers.
This case study clearly demonstrates that even a partial optimization of your industrial steam distribution systems can deliver hundreds of thousands of dollars in annual savings—while supporting green manufacturing goals and long-term sustainability.
Checklist for Industrial Steam Distribution Systems
To ensure optimal operation, industrial steam distribution systems must be inspected regularly. Scheduled maintenance of critical components prevents heat loss, reduces fuel waste, and stabilizes the entire process.
| Inspection Item | Check Frequency | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Steam traps operating correctly | Every 2 weeks | Prevent steam loss |
| Proper steam take-off location | Quarterly | Avoid condensate ingress |
| Pipe insulation quality | Every 6 months | Maintain steam temperature |
| Check valves functional | Monthly | Prevent cross-flow in steam lines |
To ensure optimal operation, industrial steam distribution systems must be inspected regularly. Scheduled maintenance of critical components prevents heat loss, reduces fuel waste, and stabilizes the entire process.
Conclusion: Small Adjustments, Big Impact
Although often considered a supporting system, an industrial steam distribution system plays a critical role in energy cost control and production efficiency. Even minor issues—such as leaky steam traps, poorly positioned steam take-offs, or lack of insulation—can silently drain hundreds of millions of VND each year without being noticed.
If your facility is encountering any of the five critical issues mentioned above, now is the time to act. Optimizing your steam distribution system not only helps reduce fuel consumption but also enhances operational stability and supports your journey toward green, efficient, and sustainable production.
Need to Audit Your Steam Distribution System?
Looking to save fuel, reduce thermal losses, and improve operational efficiency?
DIVI Group is here to help.
-
Free 1-on-1 technical consultation
-
Complimentary practical guide:
“Master Your Steam Distribution System in 7 Days” -
Tailored solutions for key sectors: textile, food processing, chemical, and industrial manufacturing
Contact Us Today:
-
Email: info@divigroup.com.vn
-
Technical Hotline: 0942 488 81
Related Articles:
Additional Reference Videos:
3 Warning Signs Your Boiler Might Explode
Why Is Fine Dust Escaping From Your Boiler Chimney? 7 Hidden Causes Explained
DIVI Group's Boiler Products:
Other news
-
Steam Separator – An Effective Solution for Dry Steam
29/12/2025, -
Treating High CO Emissions in Fixed-Grate Boilers – Is Boiler Replacement Necessary? Practical Solutions from DIVI
18/12/2025, -
What Is a Steam Trap? Principles, Types, and How to Select the Right Steam Trap for Your Steam System
07/12/2025, -
COMPARISON OF STEAM TRAPS: PRINCIPLES – EXPERIMENTS – OPTIMAL SELECTION FOR STEAM SYSTEMS
29/11/2025, -
Compact Biomass-Fired Boiler DVG-VN – The Optimal Fossil-Fuel Replacement Solution for Factories
23/11/2025, -
Which Boiler Should You Choose: Fixed Grate or Fluidized Bed? Detailed Efficiency, Cost & Environmental Comparison
24/06/2025, -
Mr. Boiler Speaks: Wake-Up Call from an Industrial Icon
09/06/2025, -
What is a Thermal Oil Heater? Structure, Benefits & Safety Tips
27/05/2025, -
3 Danger Signs of Boiler Operation You Should Never Ignore
24/05/2025, -
7 Common Causes of Boiler Flue Gas Issues – Effective Treatment Solutions
08/05/2025,

 EN
EN