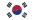
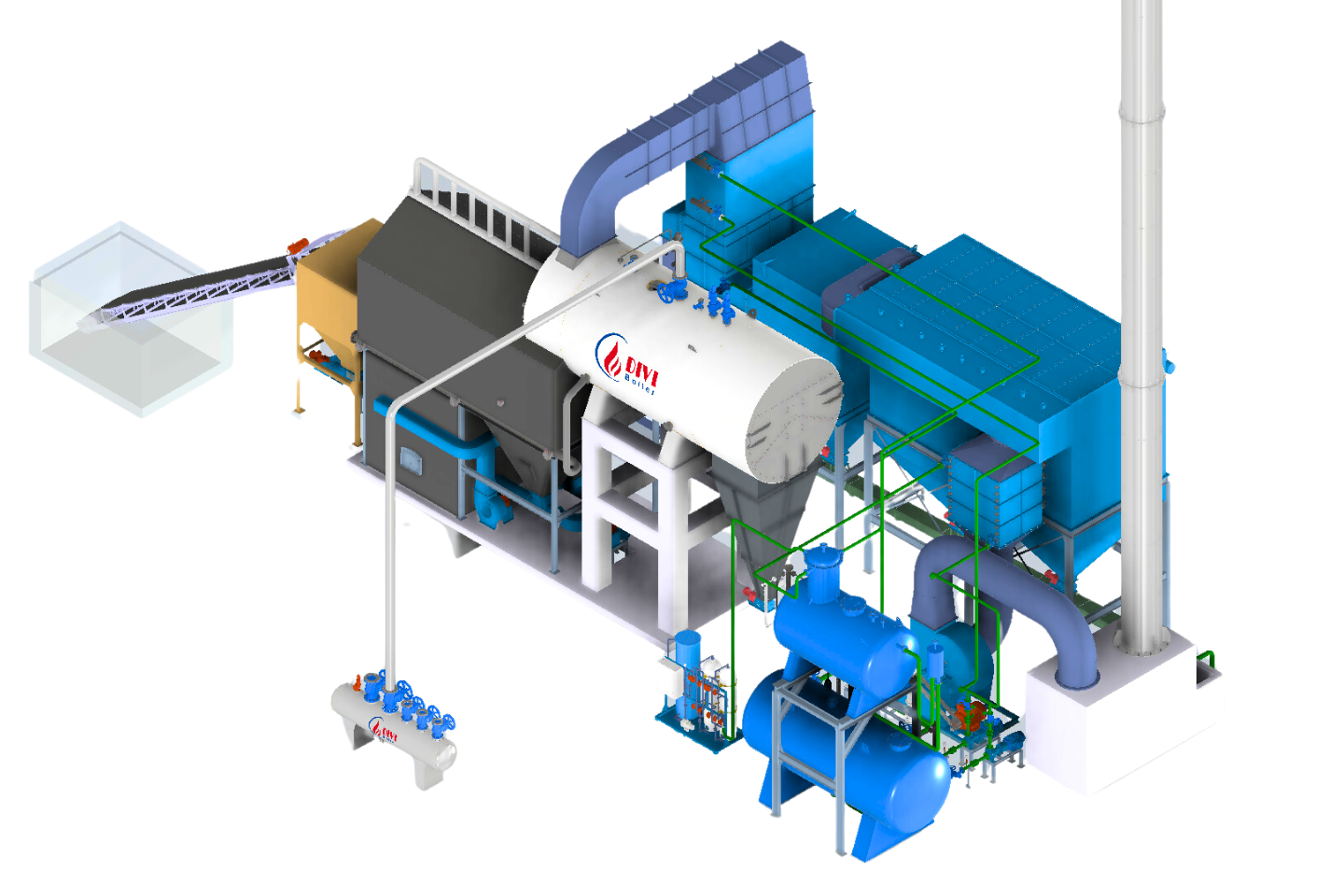
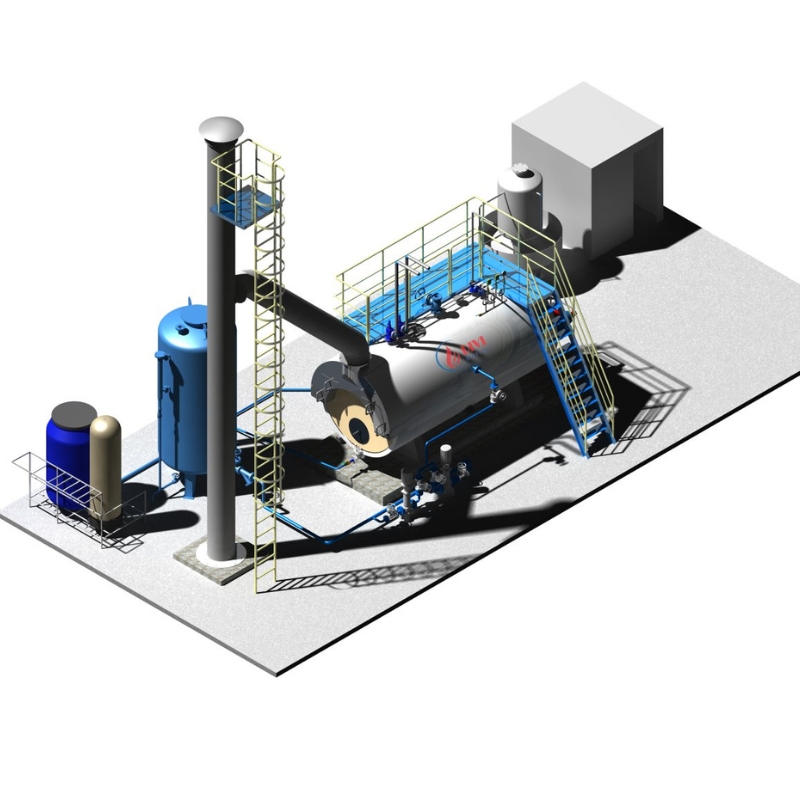
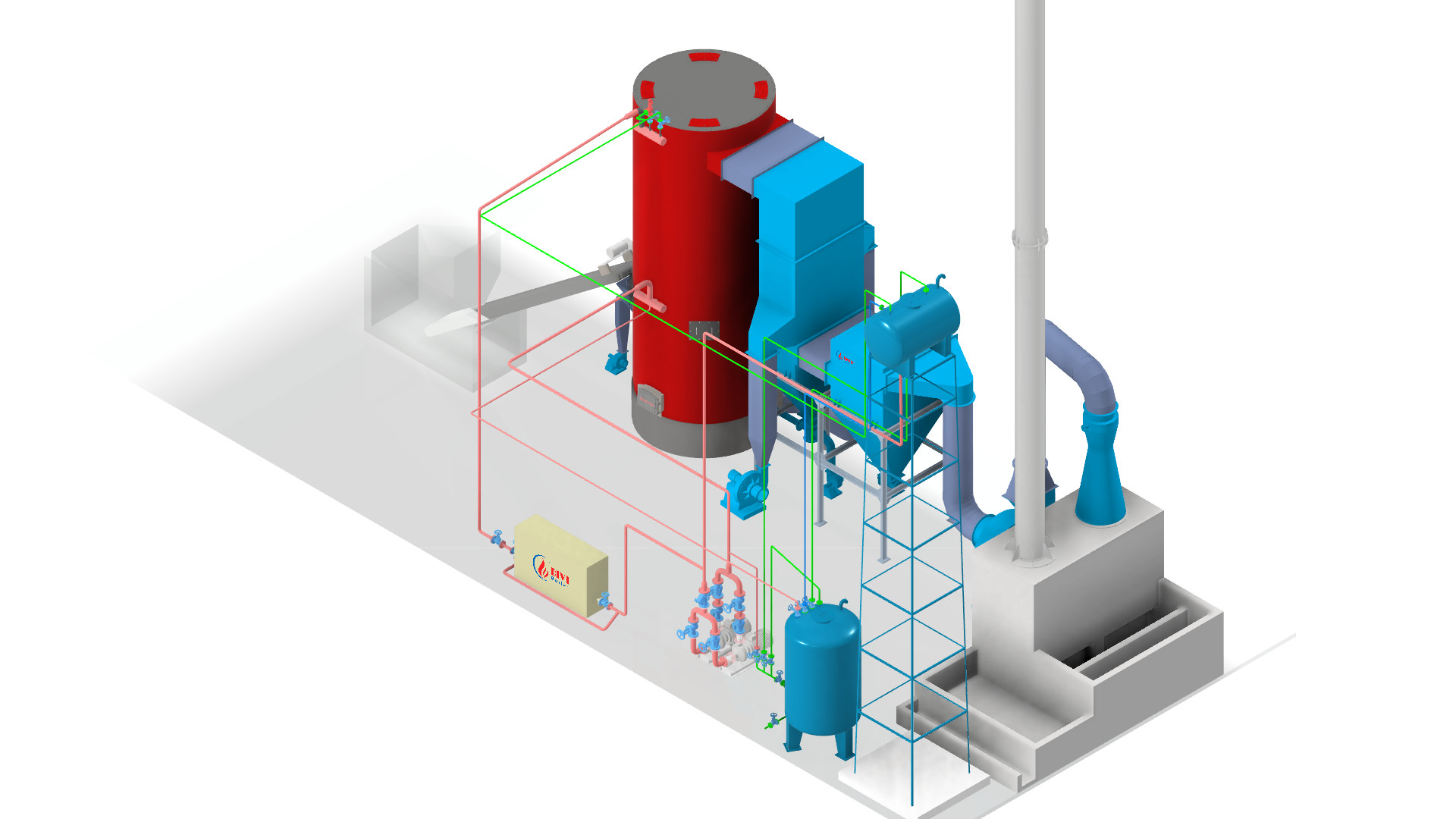
What Are the Different Types of Boilers?
What are the different types of boilers, and how do they work? Whether you're planning to upgrade your heating system or setting up a new industrial plant, understanding the types of boilers available today is crucial to ensure both efficiency and safety. In this comprehensive guide, we break down each boiler type by fuel source, pressure, and application—covering everything from different types of boilers to types of steam boilers, so you can make the most informed decision.
Introduce
In both residential and industrial settings, boilers are critical components for generating heat and steam. By burning fuels or converting electricity, they heat water to provide energy for space heating, industrial processes, or steam-driven equipment. Choosing the right boiler system not only ensures optimal performance but also helps reduce greenhouse emissions and minimize long-term costs.
There are many types of boilers available today, each designed for specific operating conditions and fuel sources. From different types of boilers for domestic use to advanced types of steam boilers for manufacturing, understanding their characteristics and distinctions is essential to select the most suitable solution for your needs.
Classification of Boilers
Understanding the different types of boilers is essential for selecting a system that fits your application, fuel availability, and performance goals. Boilers can be categorized based on fuel type, combustion method, and structural design. Below is a breakdown of the main classification types, aligned with modern industrial standards.
A. Classification by Fuel State
Understanding the types of boilers by fuel source is essential when choosing a solution that fits both technical and environmental requirements. Below are the two primary categories based on the physical state of fuel: liquid fuel and solid fuel.
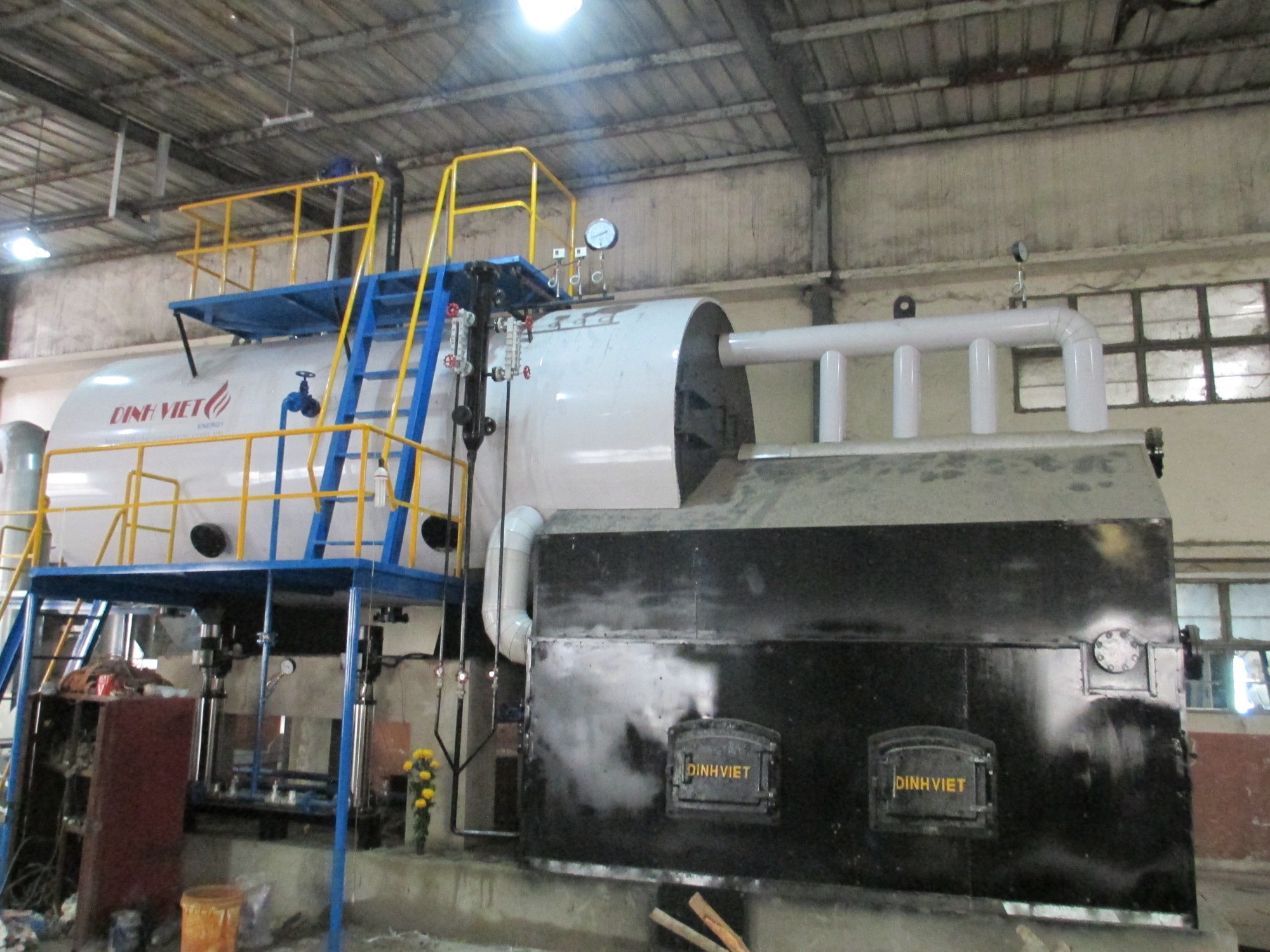
 Industrial boiler using liquid fuel
Industrial boiler using liquid fuelIf your facility demands stable pressure and high-temperature output, liquid fuel boilers are an ideal option. These systems typically burn Diesel, FO (furnace oil), or LPG, making them popular in industries such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals.
Advantages:
-
Quick startup and thermal stability
-
Compatible with automatic control systems
-
Lower particulate emissions compared to solid fuels
Environmental Impact: Modern liquid fuel boilers can meet stringent environmental standards with proper burners and emission controls, making them cleaner than traditional systems.
Solid Fuel Boilers
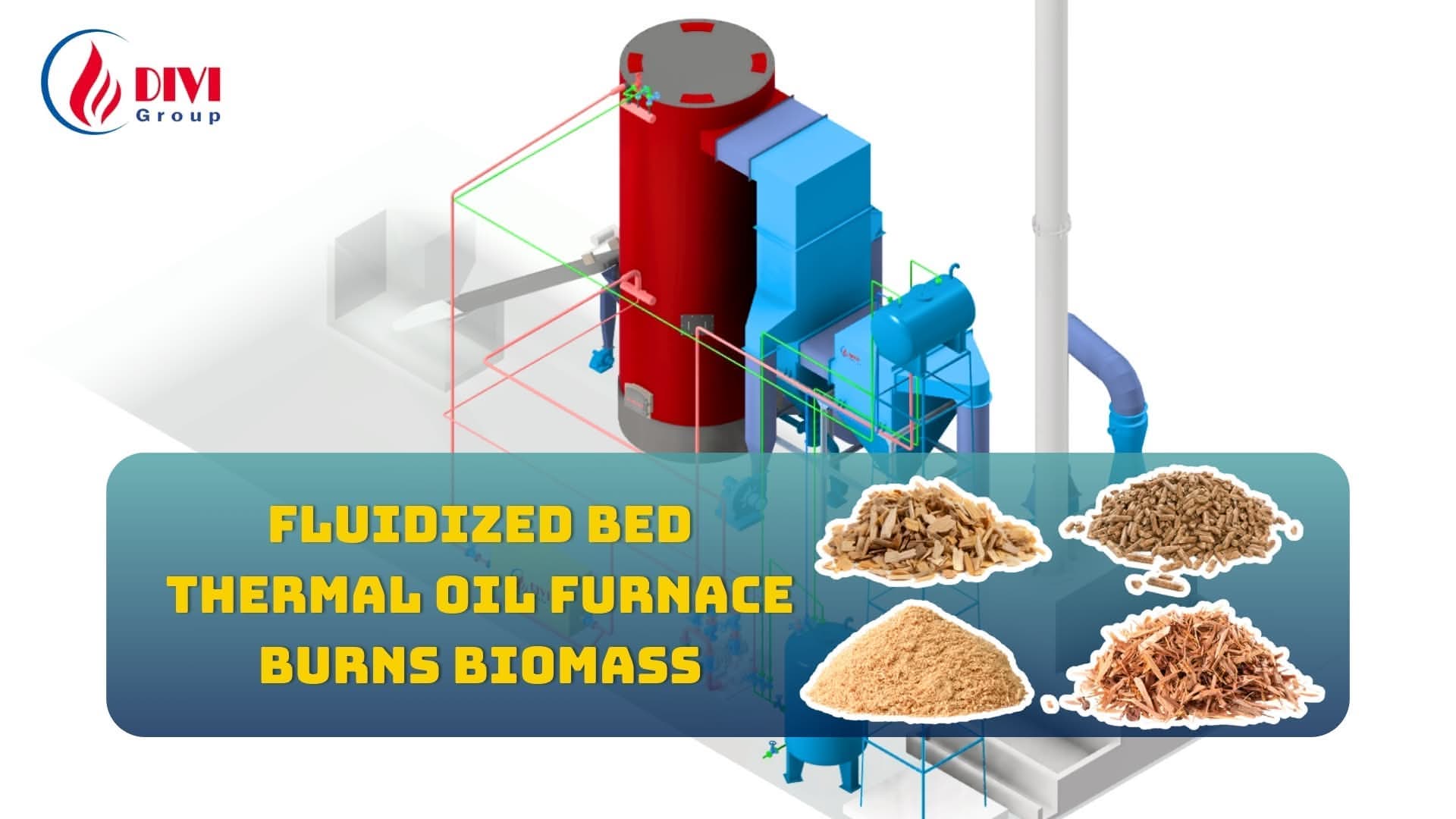
For operations with access to coal, wood, or biomass, solid fuel boilers are a cost-effective and robust choice. These are commonly used in textile, steel, and paper manufacturing, where energy demand is high and consistent.
Advantages:
-
Lower fuel costs
-
Supports renewable biomass fuels (e.g., sawdust, rice husk)
-
Ideal for regions with abundant agricultural waste
Sustainability Note: When using biomass, these types of boilers support carbon-neutral operations and contribute to Net Zero goals.
B. Classification by Solid Fuel Combustion Method
Different solid fuel boilers are further divided based on their combustion technology. These distinctions are important for operational efficiency and fuel flexibility.
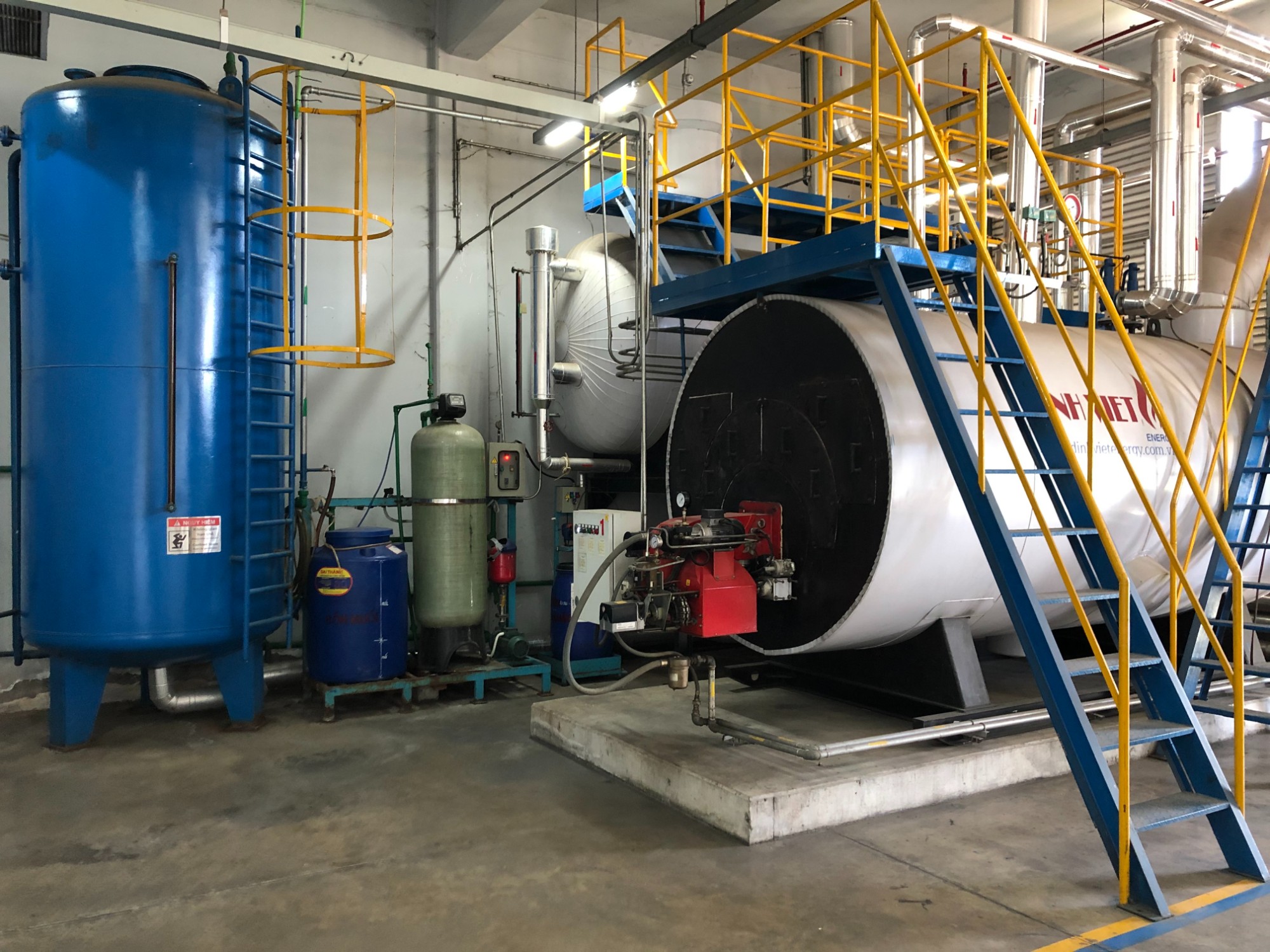
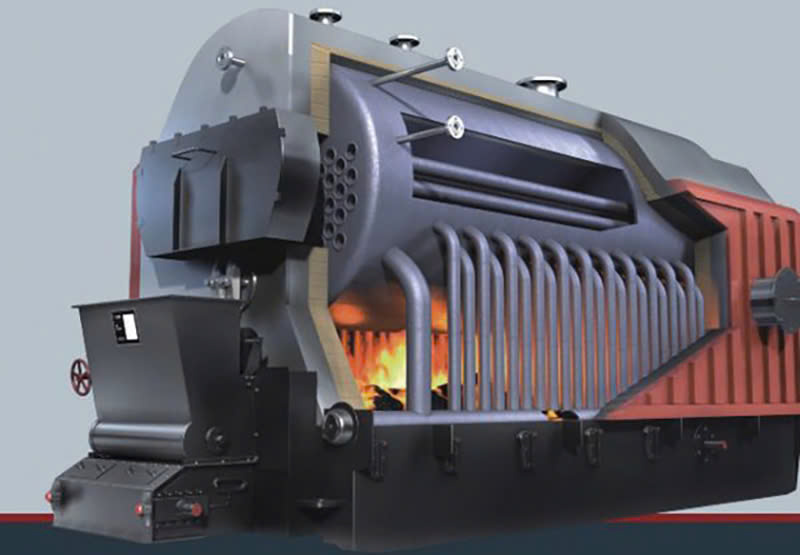
1. Fixed Grate Boilers
 Fixed grate industrial boiler
Fixed grate industrial boilerAmong the different types of boilers used in industrial applications, fixed grate boilers represent one of the most traditional and mechanically simple designs. These boilers operate with a fixed combustion grate, where solid fuels—such as wood logs, lump coal, or biomass briquettes—are manually fed and burned. While they are cost-effective and easy to construct, they require intensive manual control, including fuel loading, ash removal, and combustion regulation.
Because of their straightforward design and low automation level, fixed grate boilers are typically categorized under basic types of steam boilers used in small-scale industries, such as brick kilns, textile dyeing units, and agro-based processing plants. These industries often have moderate heat requirements and benefit from on-site fuel availability.
However, these boilers come with limitations. The manual operation leads to inconsistent combustion efficiency, higher emissions, and frequent maintenance. As a result, fixed grate systems are increasingly being replaced in modern setups by more efficient types of boilers, such as fluidized bed or chain grate boilers, which offer better fuel flexibility and automation.
Use Case: Best suited for industries with simple thermal loads, readily available low-cost fuels, and where advanced automation is not a priority.
2. Chain Grate Boilers
 Furnace of a fixed grate industrial boiler
Furnace of a fixed grate industrial boiler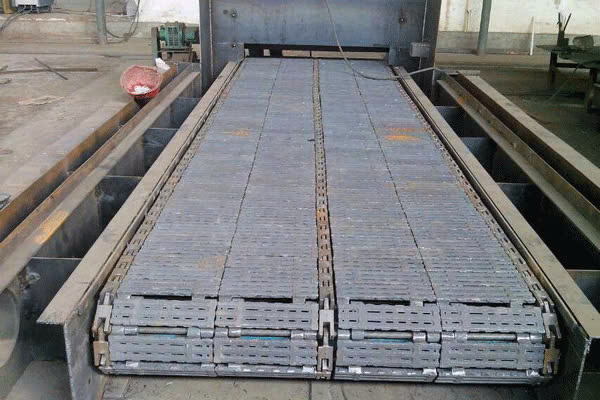  Fixed grate surface of an industrial boiler
Fixed grate surface of an industrial boiler Among the different types of boilers used in industrial operations, chain grate boilers are a widely adopted solution for burning small-particle solid fuels. These include rice husk, wood pellets, sawdust, and various forms of agricultural waste. The defining feature of this type of steam boiler is its mechanized grate system, which moves continuously to transport fuel through the combustion chamber. This setup allows for automated fuel feeding, steady burning, and consistent heat output.
Chain grate boilers offer several advantages over more traditional types of boilers, such as fixed grate systems. These advantages include higher combustion efficiency, optimized fuel usage, and significantly reduced labor costs due to minimal manual intervention. As a result, they are well-suited for operations that require continuous steam generation over long hours of production.
Because of their automation capabilities and adaptability to low-cost biomass fuels, chain grate boilers are popular in industries like food and beverage processing, textile dyeing, and rubber manufacturing—sectors where steam demand is both constant and energy-intensive.
Use Case: Ideal for medium to large-scale industrial facilities that aim to balance fuel cost, combustion efficiency, and labor savings.
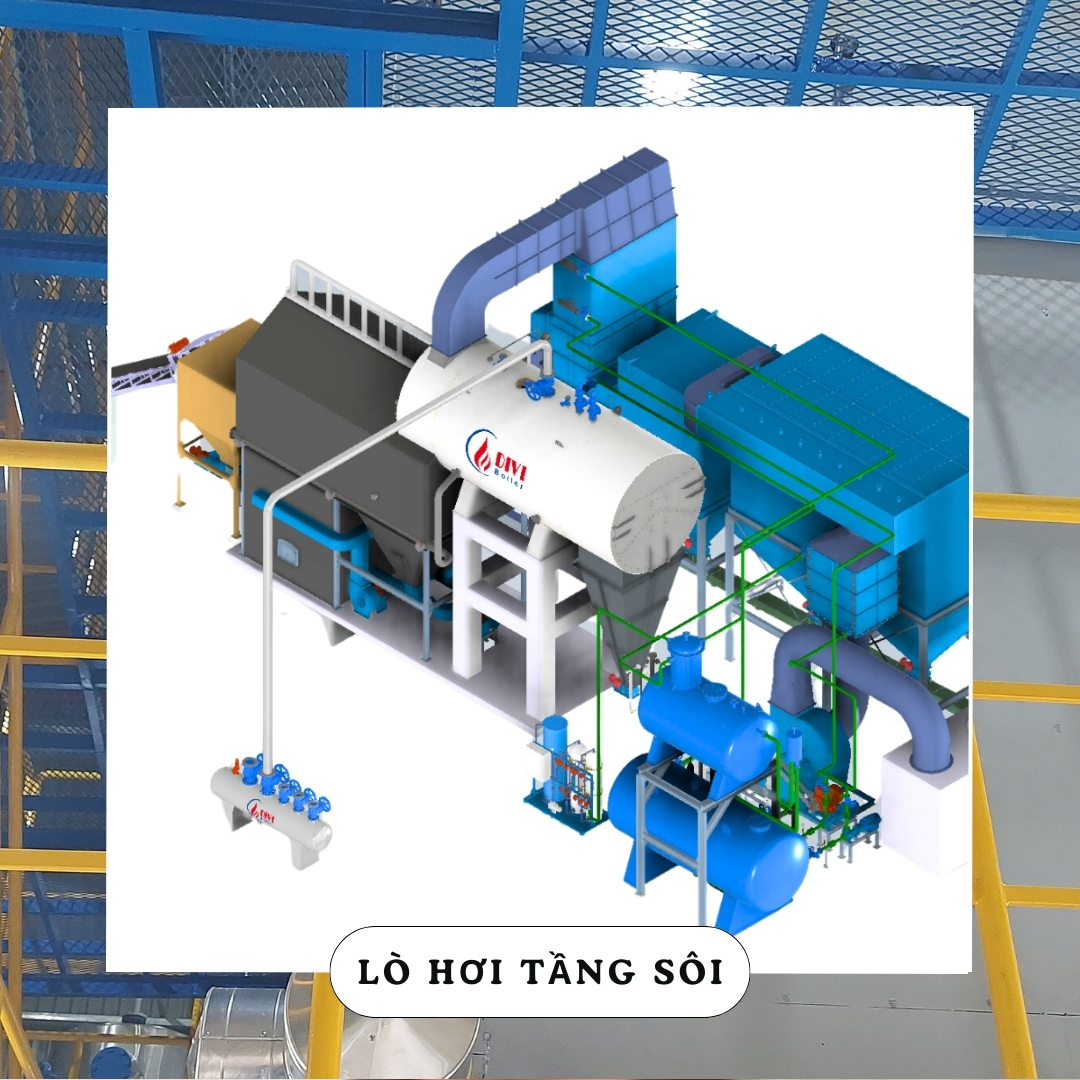
3. Fluidized Bed Boilers
Among the most advanced types of steam boilers, fluidized bed boilers stand out for their exceptional ability to burn low-grade, moisture-rich, or difficult-to-combust fuels. This type of boiler operates by suspending fuel particles in a fluidized bed of hot sand or ash, which behaves like a boiling liquid. This technique ensures even heat distribution and promotes complete combustion, even with challenging fuel types.
As part of the different types of boilers used in industrial applications, fluidized bed technology offers several major advantages. First, it maintains a uniform temperature profile throughout the combustion zone, reducing the risk of hot spots and thermal stress. Second, it produces significantly lower emissions, especially NOx (nitrogen oxides) and CO (carbon monoxide), due to controlled combustion temperatures and enhanced mixing of fuel and air. Third, it supports excellent fuel flexibility, making it ideal for plants using biomass, waste-derived fuels, or a blend of different materials.
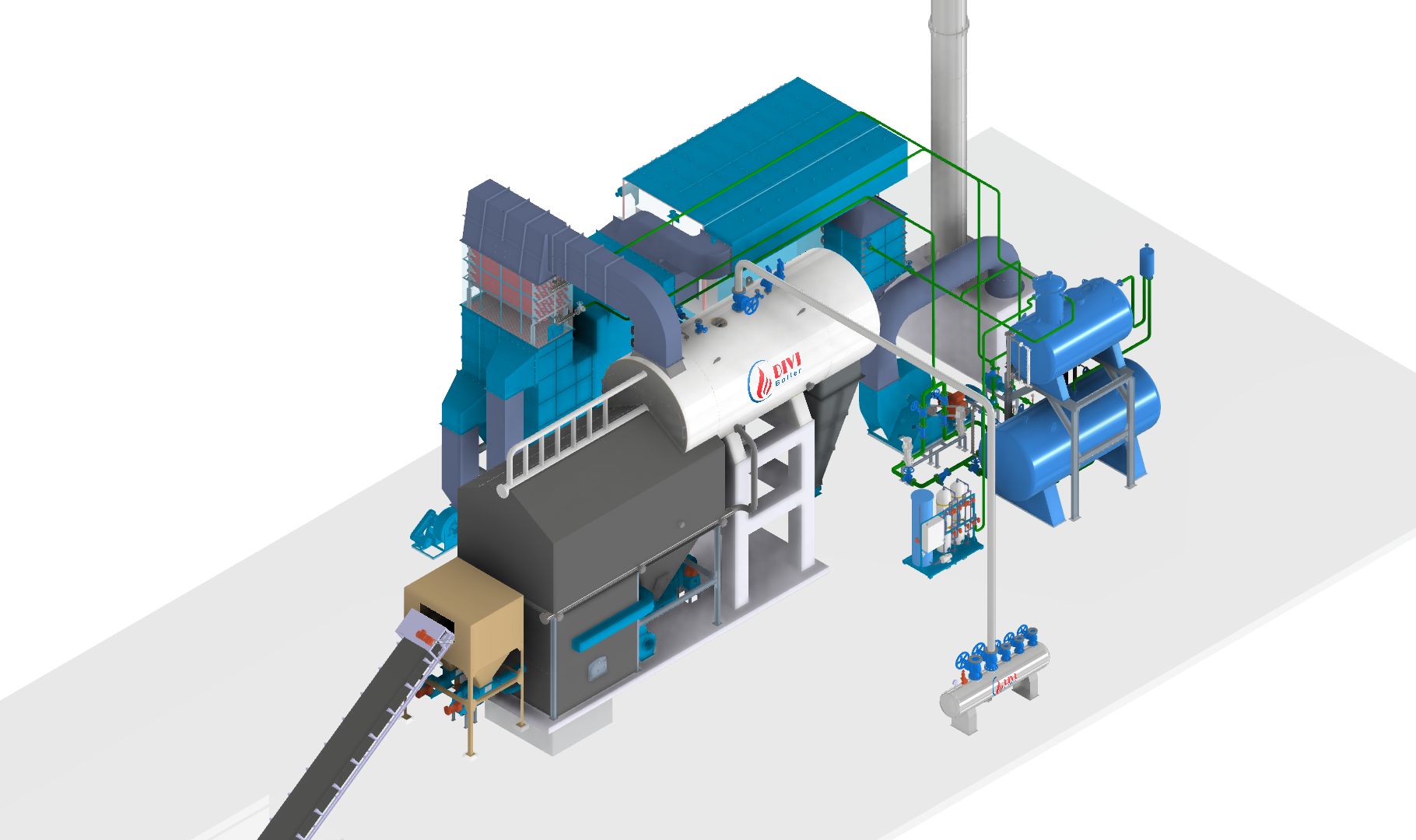 Fluidized Bed Boilers
Fluidized Bed BoilersThese characteristics make fluidized bed boilers one of the most efficient and environmentally friendly types of boilers available today. They are especially suitable for industries with variable or unstable fuel sources, such as pulp and paper mills, chemical plants, waste-to-energy facilities, and agro-industrial operations.
Use Case: Best suited for complex industrial operations seeking high efficiency, low emissions, and the ability to burn a wide range of fuels.
C. Classification by Solid Fuel Combustion Method
When exploring the different types of boilers, structural design is a key factor that affects performance, maintenance, and application range. The two most widely used designs are fire-tube boilers and water-tube boilers, each optimized for specific pressure levels and usage scenarios.
1. Fire-Tube Boilers
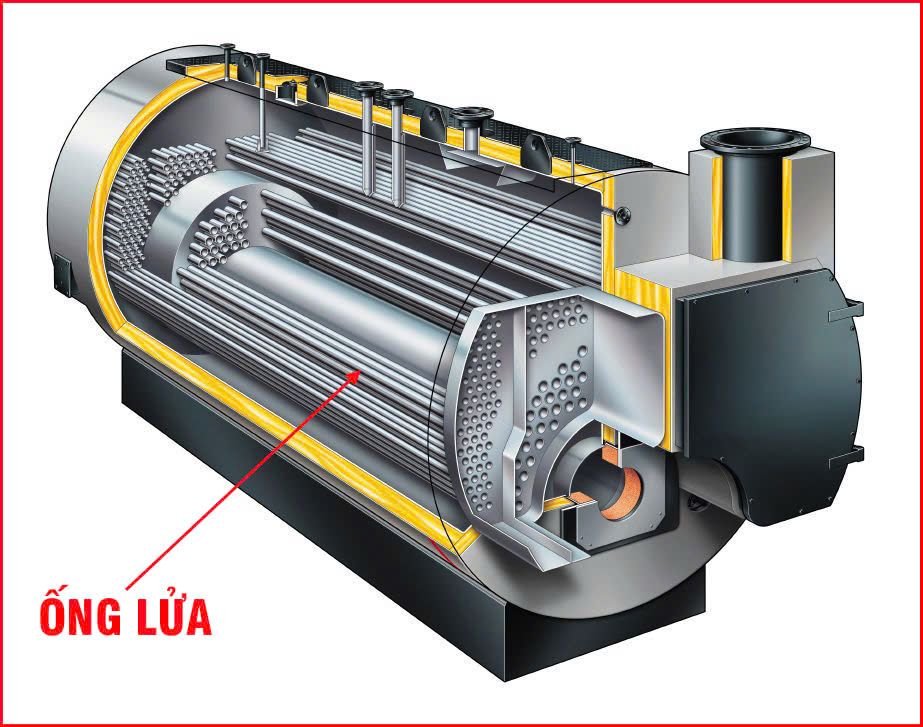 Fire-Tube Boilers
Fire-Tube Boilers
One of the most common types of boilers used in small to medium industrial operations is the fire-tube boiler. In this design, hot combustion gases pass through a series of tubes that are surrounded by water. The heat from the gases is transferred to the water, generating steam.
Advantages:
-
Low initial cost and straightforward setup
-
Easy to operate and maintain
-
Compact size suitable for limited space environments
Limitations:
-
Cannot withstand high steam pressure
-
Slower heat transfer and steam generation
Typical Use Cases: Textile mills, food processing units, light manufacturing plants.
Fire-tube systems are ideal for facilities with moderate heating needs and consistent operational conditions. Among all types of boilers, these offer simplicity but are limited in terms of pressure capacity.
2. Water-Tube Boilers
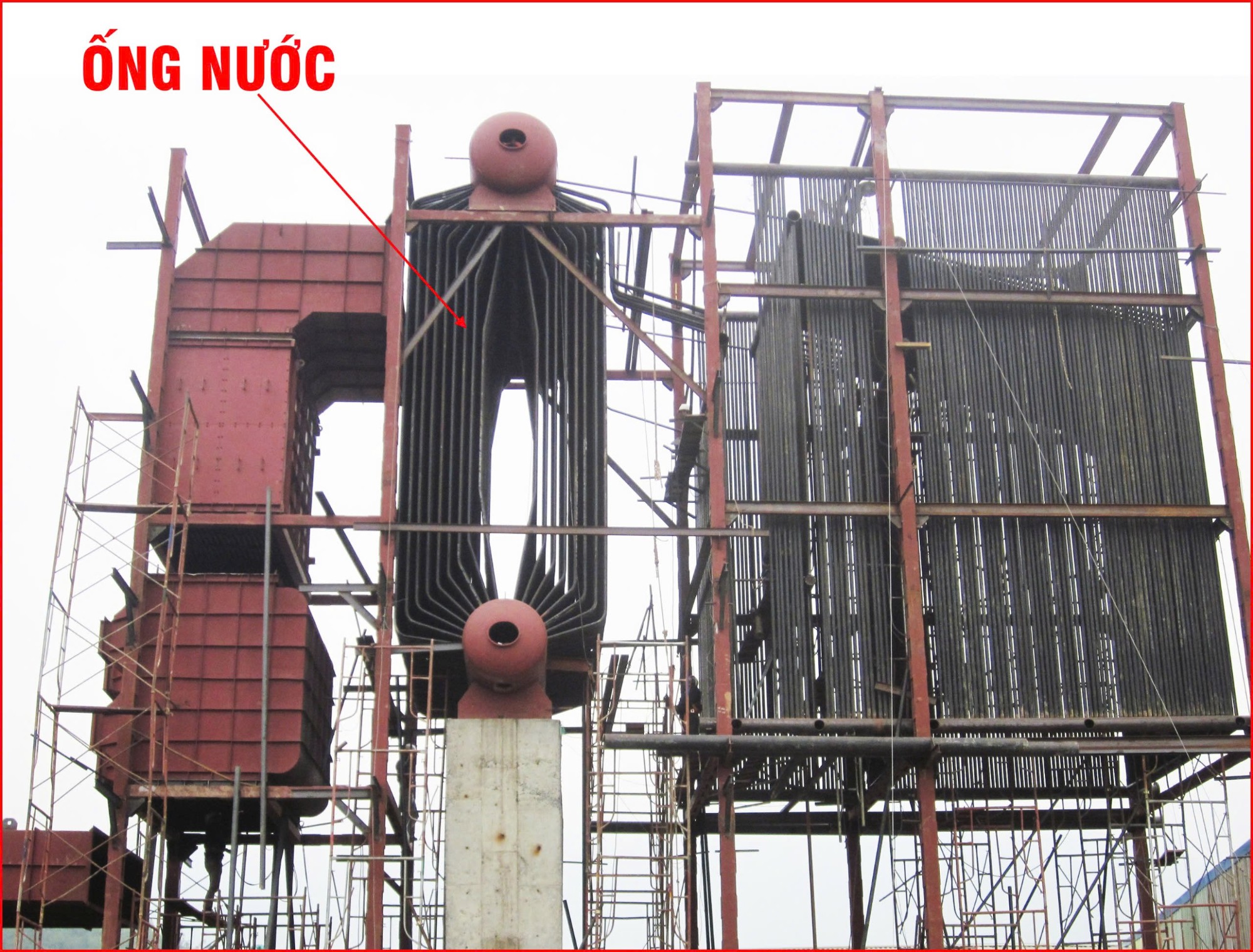 Water-Tube Boilers
Water-Tube Boilers
For applications that demand high-pressure steam and fast thermal response, water-tube boilers are among the most advanced and efficient types of steam boilers available. In this configuration, water circulates inside the tubes while combustion gases flow externally to provide heat.
Advantages:
-
Rapid steam production with high thermal efficiency
-
Capable of generating superheated steam
-
Scalable for very large capacities and continuous use
Limitations:
-
Higher installation and maintenance costs
-
Requires skilled operation and monitoring
Ideal For: Power generation facilities, petrochemical plants, high-pressure industrial systems.
As part of the different types of boilers on the market, water-tube systems are the top choice for sectors with intense steam demand and strict performance standards. Their flexibility in handling varying fuel types and pressures makes them essential in heavy-duty environments.
Key Factors When Selecting the Right Boiler
When evaluating the different types of boilers, it’s essential to consider technical, operational, and financial aspects to ensure long-term efficiency and safety.
1. Usage Needs
Do you require hot water or pressurized steam? Are you using the system for residential heating, commercial operations, or industrial production? Each application demands a different boiler configuration. For example, types of steam boilers are ideal for processing industries that rely on high-pressure steam, while hot water boilers are better suited for domestic or space heating.
2. Fuel Availability
Assess local fuel infrastructure before choosing. If natural gas is available and affordable, gas boilers are an efficient choice. In off-grid areas, diesel, LPG, or biomass may be more practical. For emissions-sensitive zones, electric boilers offer clean operation.
3. Energy Efficiency
Opt for condensing boilers where possible. These systems recover waste heat from flue gases, improving overall thermal efficiency and reducing operating costs. Many types of boilers now include smart controls to optimize fuel consumption.
4. Maintenance Simplicity
Complex boiler systems often require specialized technicians and higher maintenance budgets. Simpler units—like fire-tube boilers—tend to have lower maintenance needs, making them suitable for facilities with limited technical resources.
5. Initial and Lifecycle Cost
Evaluate both upfront investment and long-term operational expenses. A higher-cost water-tube boiler may deliver better fuel economy and longevity, making it more cost-effective over a 10–15 year period.
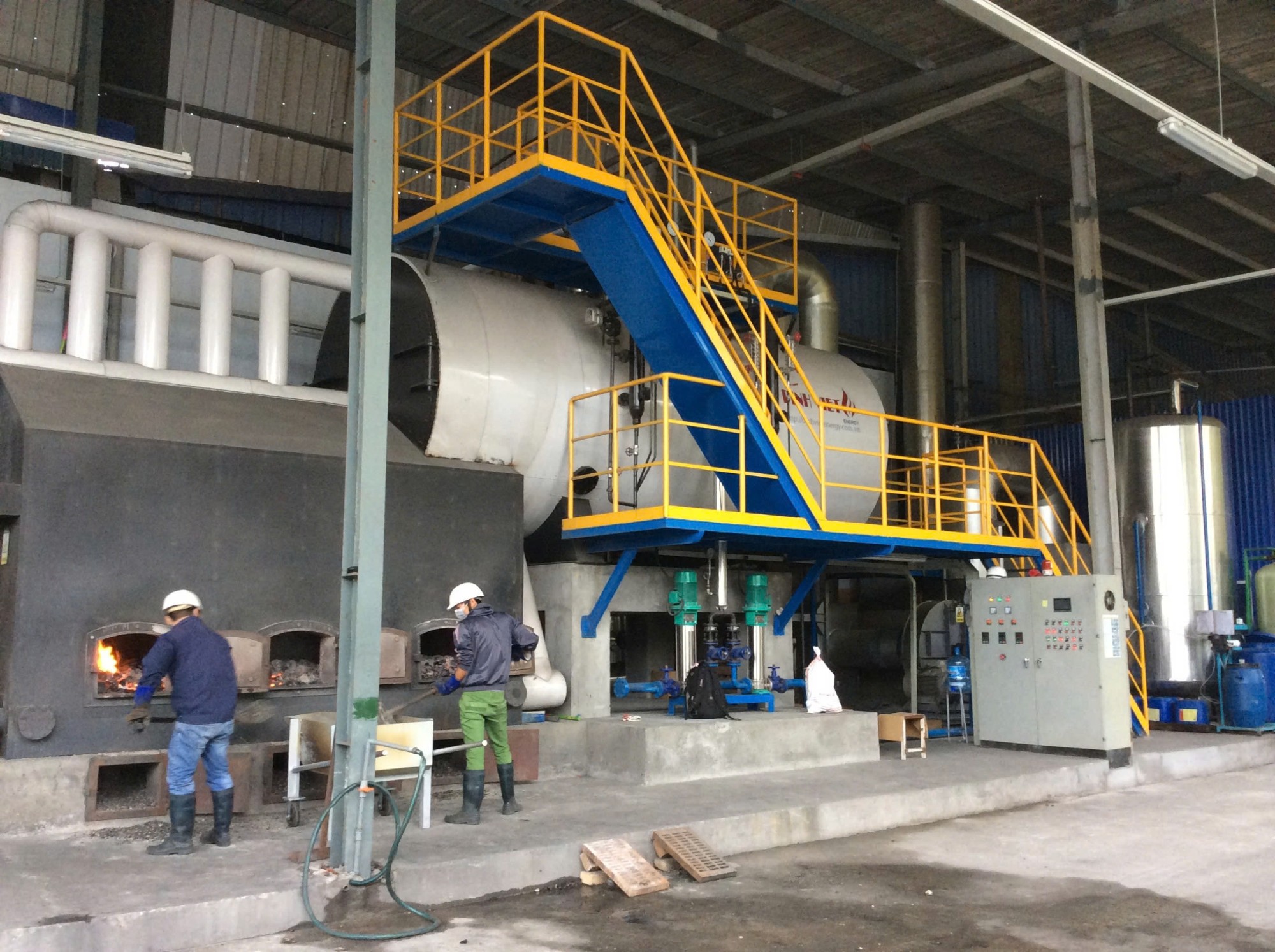
Safe Operation of Industrial Boilers and Common Hazards to Avoid
Industrial boilers—also known as steam boilers or process boilers—are critical to a wide range of manufacturing sectors. However, improper operation, poor maintenance, or non-compliance with safety standards can lead to severe consequences, including boiler explosions, equipment damage, and life-threatening injuries.
One of the most serious risks associated with certain types of boilers is pressure explosion. This typically occurs when the boiler is made from substandard materials, or routine inspections are neglected. In many cases, the safety valve—a crucial component that releases excess pressure—fails to activate properly, allowing internal pressure to rise beyond acceptable limits.
Aside from explosions, steam leakage from poorly sealed valves or pipelines can cause serious burn injuries to operators. In solid fuel systems, burning embers can eject through the furnace door, posing a risk of physical trauma. For electric-powered types of steam boilers, improper insulation or unregulated installation may lead to electrical shocks, especially in humid environments.
 Safe operation of industrial boilers
Safe operation of industrial boilersAnother often-overlooked danger is the working environment surrounding the boiler. This area often contains fine particulate matter, toxic gases such as CO and CO₂, and excessive heat radiation. Long-term exposure can result in chronic health conditions if not properly mitigated.
To reduce these risks, businesses should adopt a comprehensive safety strategy:
-
Conduct scheduled inspections of key components like safety valves, burners, and control systems.
-
Adhere to certified installation standards for all types of boilers, especially high-pressure types of steam boilers.
-
Install effective ventilation systems to minimize toxic gas concentration and maintain air quality.
-
Implement structured training programs to equip operators with knowledge of potential hazards and emergency procedures.
-
Ensure all electrical interfaces are moisture-proof and comply with industry regulations.
The Value of DIVI Group’s Industrial Boilers
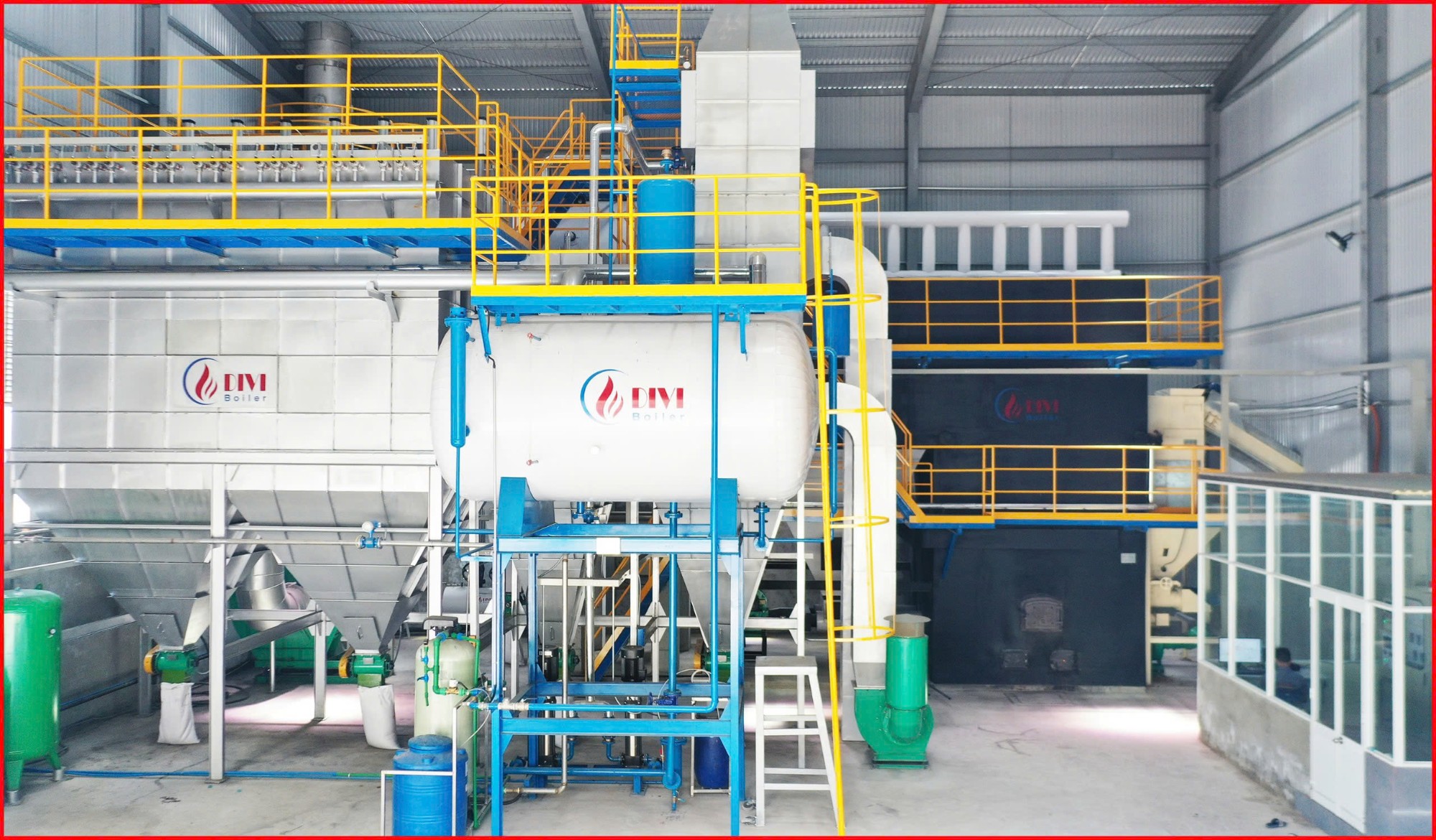

At DIVI Group, we go beyond supplying industrial boilers. Our mission is to deliver end-to-end steam solutions that help businesses optimize their operations, lower production costs, and meet environmental compliance goals.
With years of experience across multiple industries, we design and manufacture a wide range of different types of boilers, including custom-built types of steam boilers tailored to your process requirements. Our systems are engineered to meet international standards, with enhanced safety features and high fuel efficiency.
Why Choose DIVI Group?
-
Full-cycle support: from design and installation to ongoing maintenance
-
Diverse portfolio of types of boilers for every industry and energy source
-
Expertise in biomass, LPG, diesel, and low-emission boiler technologies
-
Commitment to safety, sustainability, and client success
Conclusion:
Navigating the wide array of different types of boilers requires careful evaluation of your technical requirements, fuel availability, and sustainability objectives. From compact electric models to high-capacity types of steam boilers for industrial facilities, there is a configuration to match every operational need.
By understanding how the types of boilers differ in design, output, and environmental impact, you can make a well-informed decision that maximizes efficiency while reducing costs and emissions.
Ready to find the perfect boiler for your facility? Contact our specialists today for personalized consultation and system design.
Choosing between the many different types of boilers depends on your application, efficiency goals, and environmental priorities. Whether you’re comparing types of steam boilers for industrial use or selecting a home heating solution, understanding each type’s capabilities is essential.
Explore your boiler options today—contact our experts for tailored advice!
Frequently asked questions (FAQ):
1. What are the most common types of boilers?
The most widely used types of boilers include fire-tube boilers, water-tube boilers, electric boilers, and various types of steam boilers for industrial applications. Each is tailored to different operating conditions and energy needs.
2. How can I select the right boiler for my home or factory?
Start by identifying whether you need steam or hot water, and assess your available fuel sources (gas, oil, biomass, or electricity). From there, evaluate pressure requirements, space constraints, and maintenance capacity to narrow down the best option among the different types of boilers.
3. What is the key difference between steam and hot water boilers?
Types of steam boilers are designed to produce pressurized steam for mechanical use or process heating. In contrast, hot water boilers are used to heat water for space heating or domestic consumption.
4. Which boiler type is the most environmentally friendly?
Boilers powered by renewable electricity or biomass typically offer the lowest carbon emissions. Among the types of boilers, these options are most aligned with sustainability goals.
5. Can industrial boilers operate on renewable energy?
Yes. Many types of steam boilers can be adapted to run on biomass fuels, such as rice husk or wood pellets. Electric boilers can also use power generated from solar, wind, or hydroelectric sources.
Related Articles:
Additional Reference Videos:
Prevent Boiler Explosions: Essential Safety Tips from DIVI
Operate Your Boiler Safely: 2 Simple Steps You Must Follow
DIVI Group's Boiler Products:
Other news
-
Steam Separator – An Effective Solution for Dry Steam
29/12/2025, -
Treating High CO Emissions in Fixed-Grate Boilers – Is Boiler Replacement Necessary? Practical Solutions from DIVI
18/12/2025, -
What Is a Steam Trap? Principles, Types, and How to Select the Right Steam Trap for Your Steam System
07/12/2025, -
COMPARISON OF STEAM TRAPS: PRINCIPLES – EXPERIMENTS – OPTIMAL SELECTION FOR STEAM SYSTEMS
29/11/2025, -
Compact Biomass-Fired Boiler DVG-VN – The Optimal Fossil-Fuel Replacement Solution for Factories
23/11/2025, -
Which Boiler Should You Choose: Fixed Grate or Fluidized Bed? Detailed Efficiency, Cost & Environmental Comparison
24/06/2025, -
5 Common Mistakes in Industrial Steam Distribution Systems
11/06/2025, -
Mr. Boiler Speaks: Wake-Up Call from an Industrial Icon
09/06/2025, -
What is a Thermal Oil Heater? Structure, Benefits & Safety Tips
27/05/2025, -
3 Danger Signs of Boiler Operation You Should Never Ignore
24/05/2025,

 EN
EN