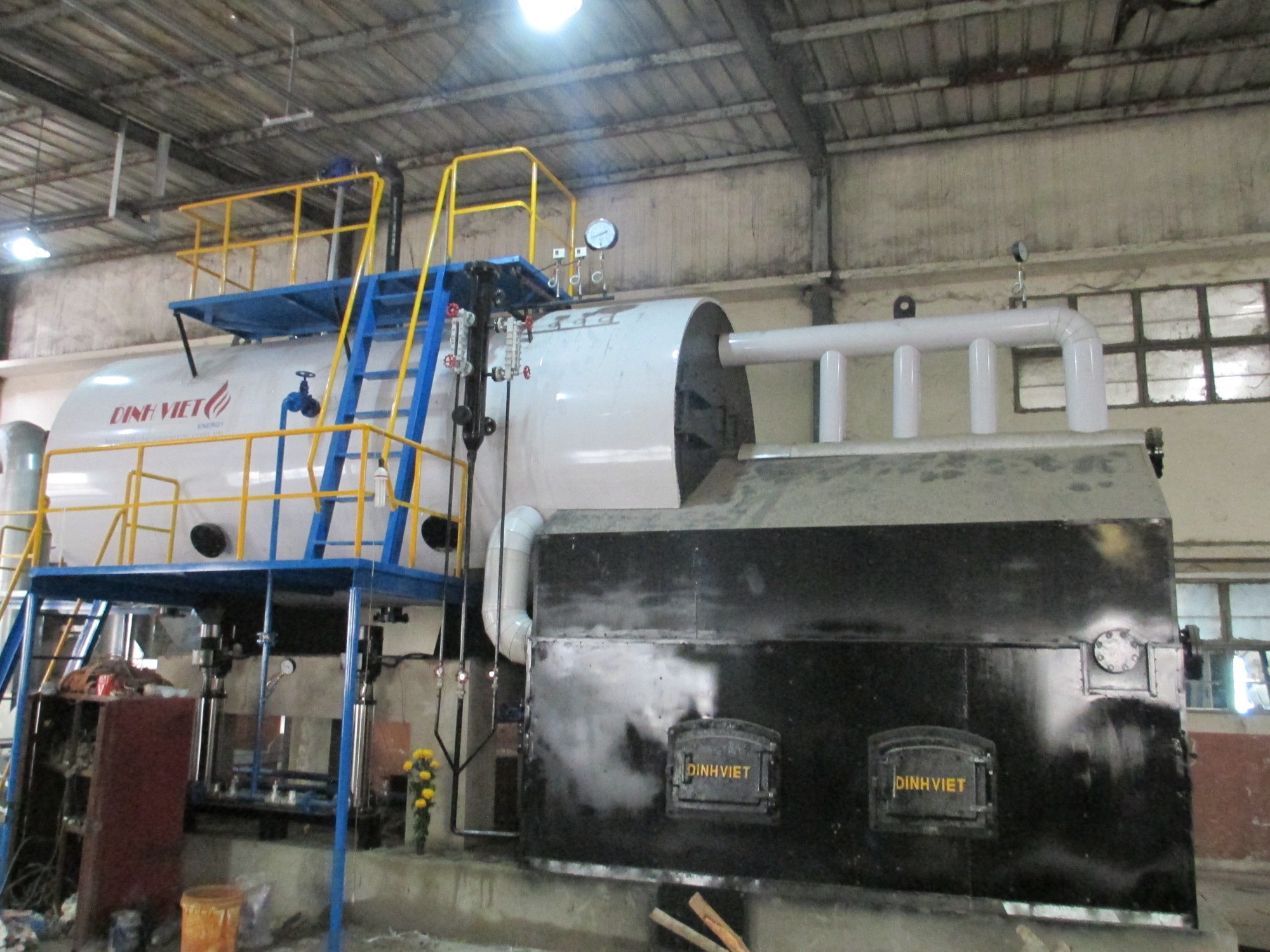
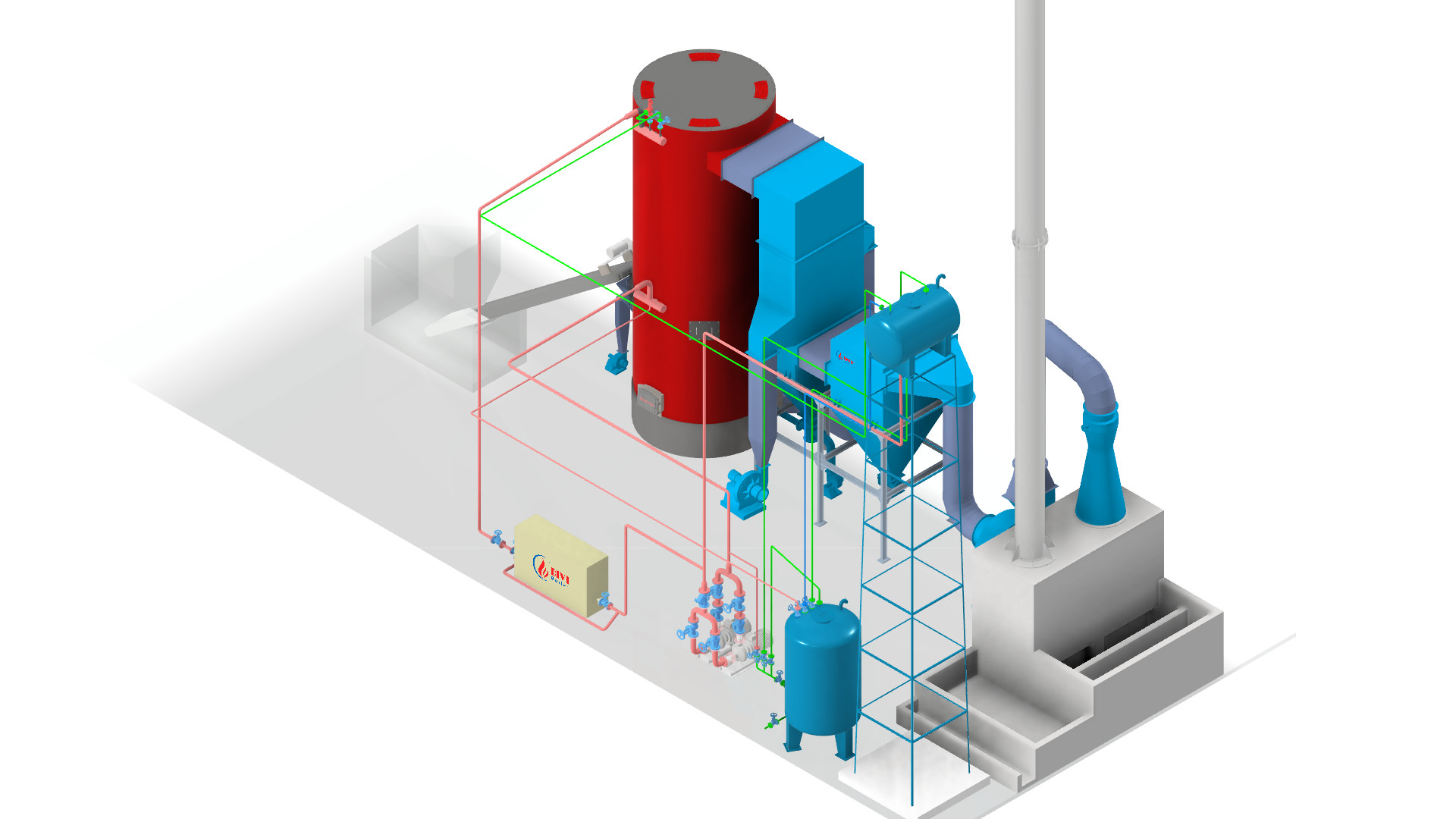
Which Boiler Should You Choose: Fixed Grate or Fluidized Bed? Detailed Efficiency, Cost & Environmental Comparison
Looking for the right steam boiler? Should you invest in a fixed grate boiler or a fluidized bed boiler? This guide helps you compare cost, efficiency, and environmental impact to select the best boiler system for your plant.
1. Investment Cost Analysis
1. Why is investment cost critical?
The initial investment cost determines project feasibility, payback period, and automation level. Choosing the right boiler technology helps you save budget and optimize long-term operational costs.
2. Detailed Cost Comparison: Fixed Grate vs. Fluidized Bed
| Category | Fixed Grate Boiler | Fluidized Bed Boiler |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Design | Simple, minimal accessories | Complex, many supplementary systems |
| Boiler Height | ~4–5 meters | ~10–13 meters |
| Fuel Feeding | Manual | Automatic via conveyor/screw feeder |
| Controls | Usually no PLC | Integrated PLC, SCADA, VFD |
| Flue Gas Treatment | May not meet latest standards | Fully compliant with QCVN 19:2024 |
| Foundation Cost | Low | Higher due to heavier structure |
| Total Cost | ~30–40% lower | Higher upfront but recouped over time |
2. Floor Space Comparison
Fixed grate boilers require about 70 m² for a 5 ton/h system thanks to simpler design. Fluidized bed boilers, with more auxiliary systems (e.g. fuel feeding, combustion chamber, flue gas treatment), need ~160 m² for the same capacity.
Tip: Limited space? Fixed grate offers flexibility. Sufficient space? Fluidized bed delivers better efficiency and compliance.
3. Compare Boiler Efficiency: Which Boiler Should You Choose for Maximum Fuel Savings?
Boiler combustion efficiency directly affects fuel consumption, steam production cost, and pressure stability in industrial operations. This makes efficiency a key factor when deciding which boiler you should choose.
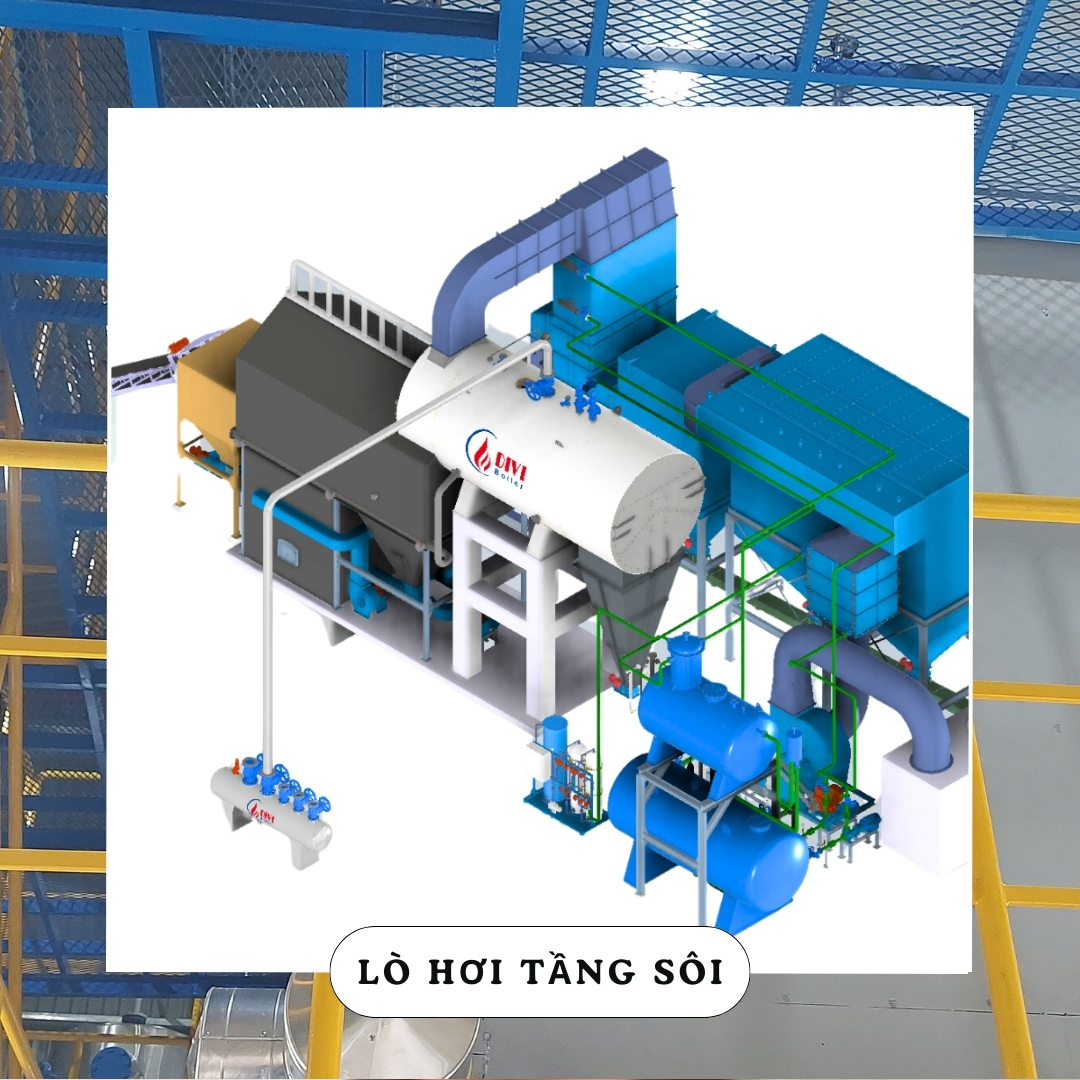
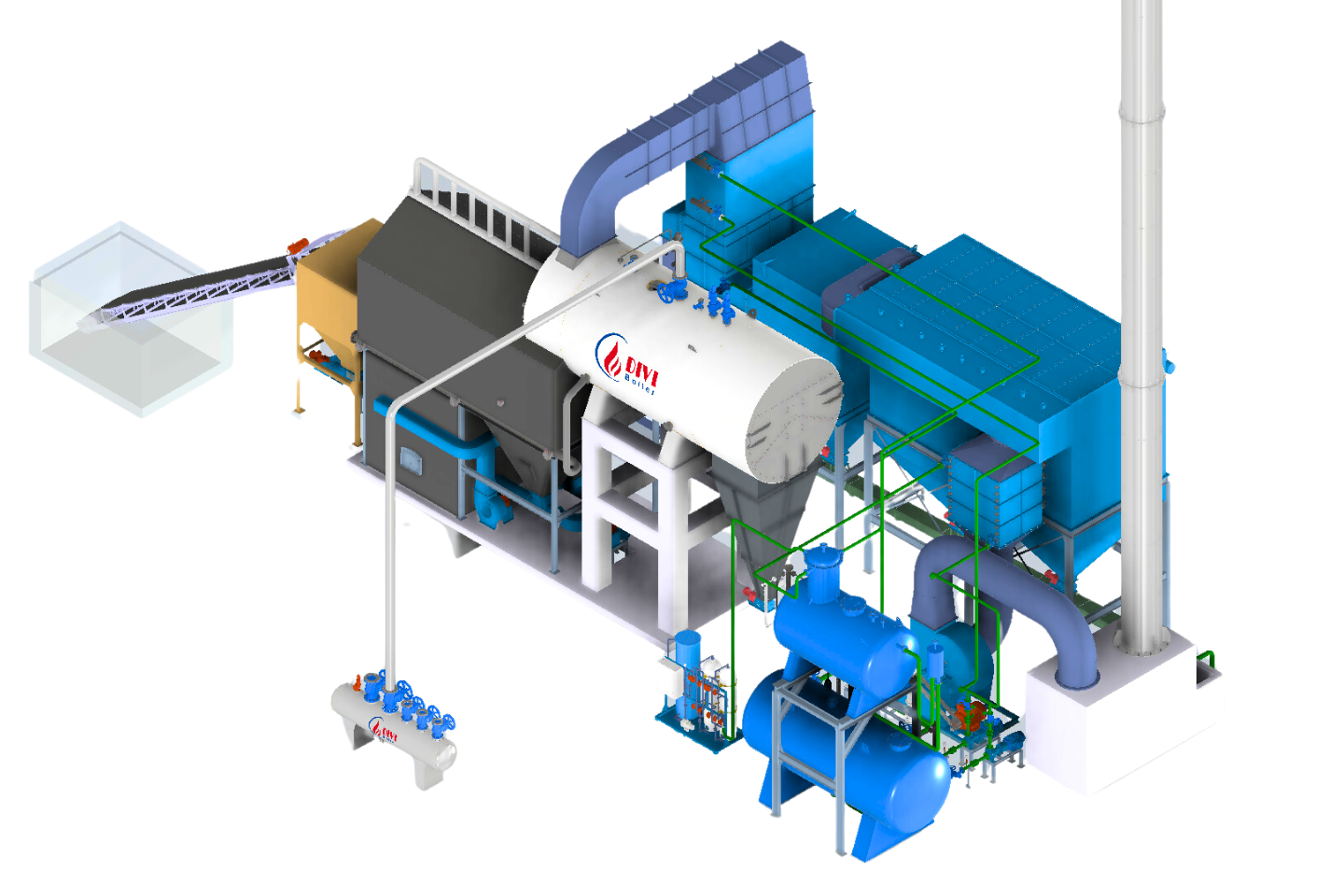
1. Fluidized Bed Boiler: Outstanding Efficiency with Advanced Combustion Technology
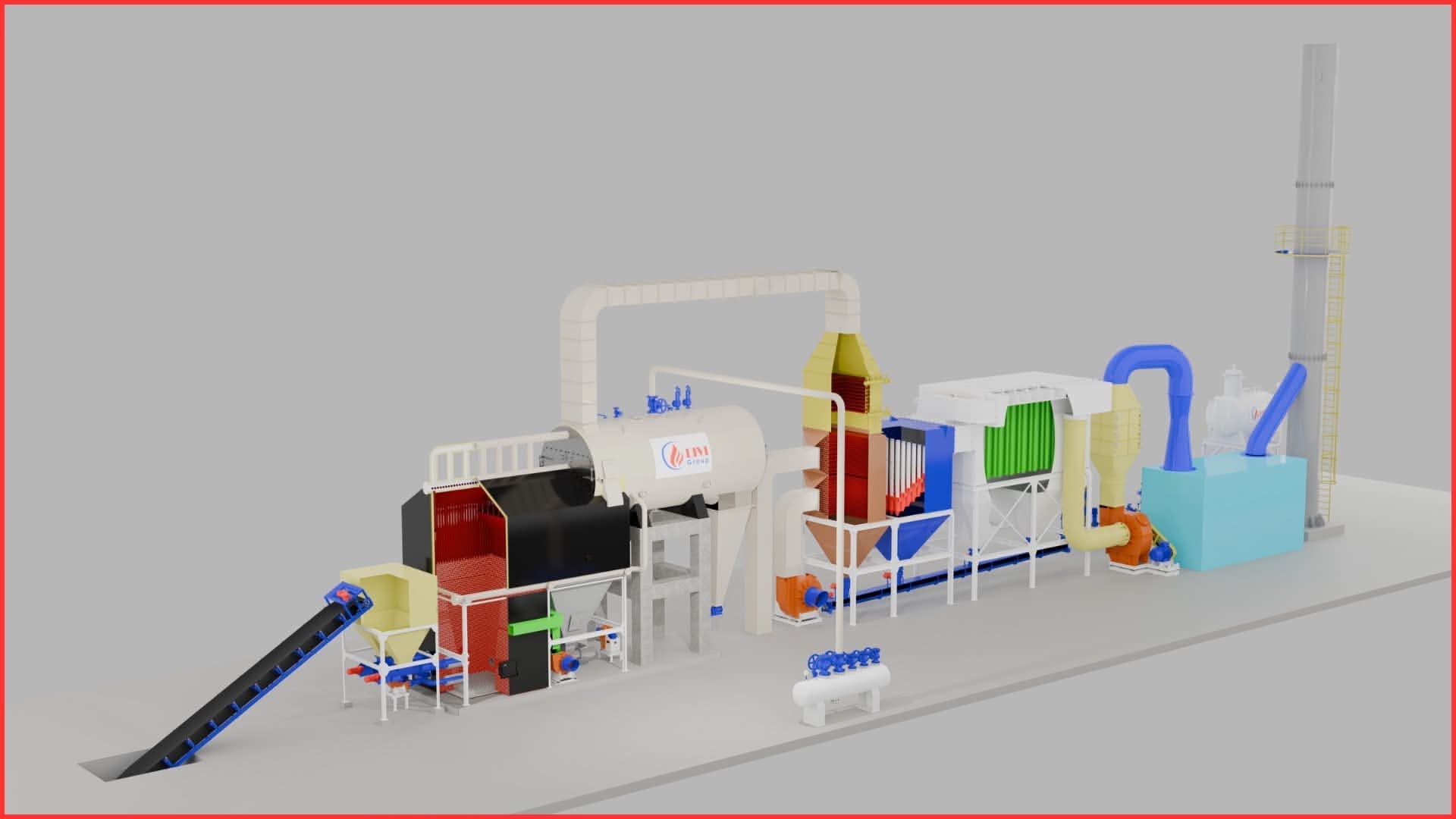 Fluidized Bed Boiler
Fluidized Bed Boiler-
The fluidized bed boiler achieves a combustion efficiency of over 85%.
-
It features a dedicated combustion chamber below the steam generation tubes.
-
Fuel burns thoroughly at optimal intensity before heat exchange begins.
-
The automatic fuel feeding system works based on steam pressure signals, ensuring the right amount of fuel at the right time.
-
The fluidized bed mechanism continuously mixes air and fuel.
-
lower CO emissions, higher combustion efficiency, and fuel savings.
2. Fixed Grate Boiler: Limited by Manual Feeding and Basic Design
 The fixed grate boiler
The fixed grate boiler-
The fixed grate boiler typically reaches only ~70% efficiency.
-
It combines combustion and steam generation in a single chamber, which reduces heat transfer performance.
-
Manual fuel feeding relies on operator experience, making it hard to control the precise fuel quantity.
-
Large air holes (30–50 mm) in the grate plate fail to distribute airflow evenly.
-
Poor air-fuel mixing leads to red flame, higher toxic emissions, and fuel waste.
| Criteria | Fluidized Bed Boiler | Fixed Grate Boiler |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion Efficiency | >85% | ~70% |
| Combustion Chamber Design | Separate from steam chamber | Integrated with steam chamber |
| Fuel Feeding | Automatic, sensor-based | Manual, operator-dependent |
| Air-Fuel Mixing | Continuous and optimized | Poor and inconsistent |
| Fuel Consumption | Lower | Higher |
4. Automatic or Manual Fuel Feeding – Key Factor When Choosing Fixed Grate or Fluidized Bed Boiler
When evaluating which boiler you should choose between a fixed grate boiler and a fluidized bed boiler, the decision is not solely based on initial investment cost. The fuel feeding method plays a major role, as it directly impacts combustion efficiency, fuel consumption, and long-term operating cost.
A fixed grate boiler uses a manual fuel feeding system, meaning operators must physically load firewood or coal into the furnace in batches.
 Automatic fuel feeding system
Automatic fuel feeding systemThis disrupts the combustion process and often results in uneven fuel input, leading to fuel waste and thermal overload. It also puts significant pressure on the operators, especially for boilers with a capacity of ≥5 tons/h, making it challenging and labor-intensive to maintain stable operation.
In contrast, a fluidized bed boiler burning biomass is equipped with a fully automatic fuel feeding system. This system operates based on signals from steam pressure sensors inside the boiler. When steam demand increases, the system automatically speeds up the conveyor or screw feeder to deliver more biomass fuel into the furnace. When the pressure reaches the set point, fuel feeding slows down or pauses—ensuring fuel is used at the right time and in the right quantity. This leads to significant fuel savings while maintaining stable combustion efficiency.
This is one of the most critical factors when comparing a fixed grate boiler and a fluidized bed boiler. If you are wondering which boiler you should choose for your plant, remember: Automatic fuel feeding not only optimizes the combustion process but also helps reduce environmental risks caused by incomplete combustion and CO emissions.
5. Flue Gas Emissions – Which Boiler Should You Choose to Meet New QCVN Standards?
Which boiler is more environmentally friendly? This is a critical factor when deciding which boiler you should choose, especially as emission regulations become increasingly stringent.
1. Issue 1 – Particulate Emissions in Hot Flue Gas
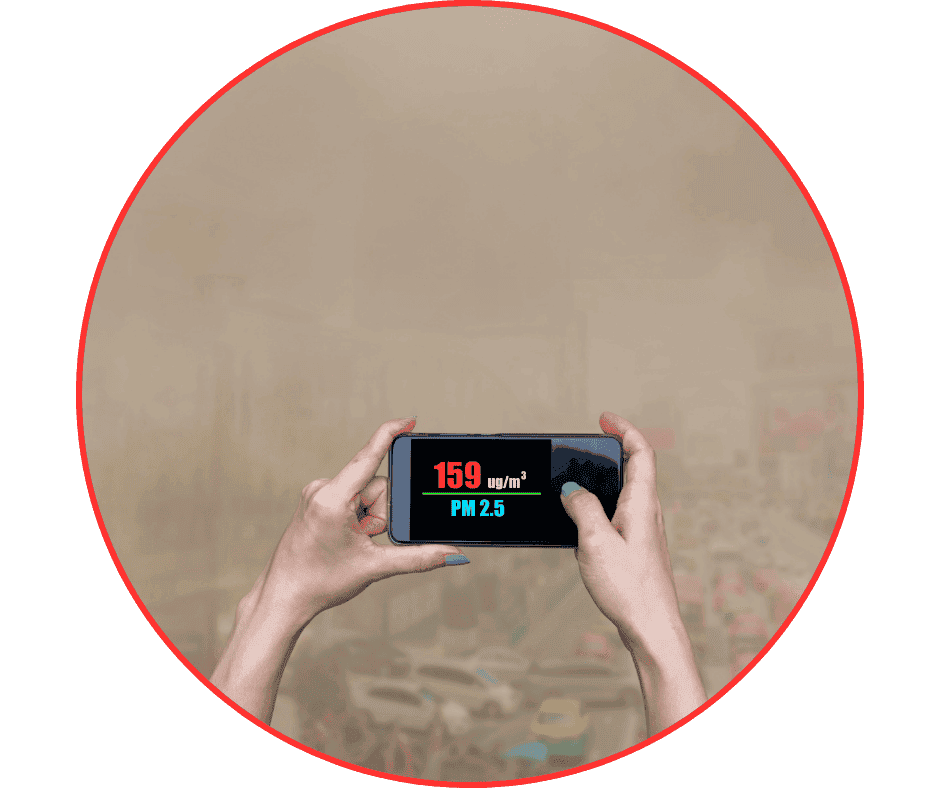 Particulate emissions in hot flue gas
Particulate emissions in hot flue gasWhen using fuels with high ash content or that generate fine dust (such as rice husk, sawdust, or fine coal), the fixed grate boiler struggles to meet the dust concentration limits specified in the QCVN standards.
The reason: The cyclone dust collector in fixed grate boilers is often basic in design, making it difficult to effectively control fine dust without additional filtration equipment.
2. Issue 2 – Harmful CO Emissions
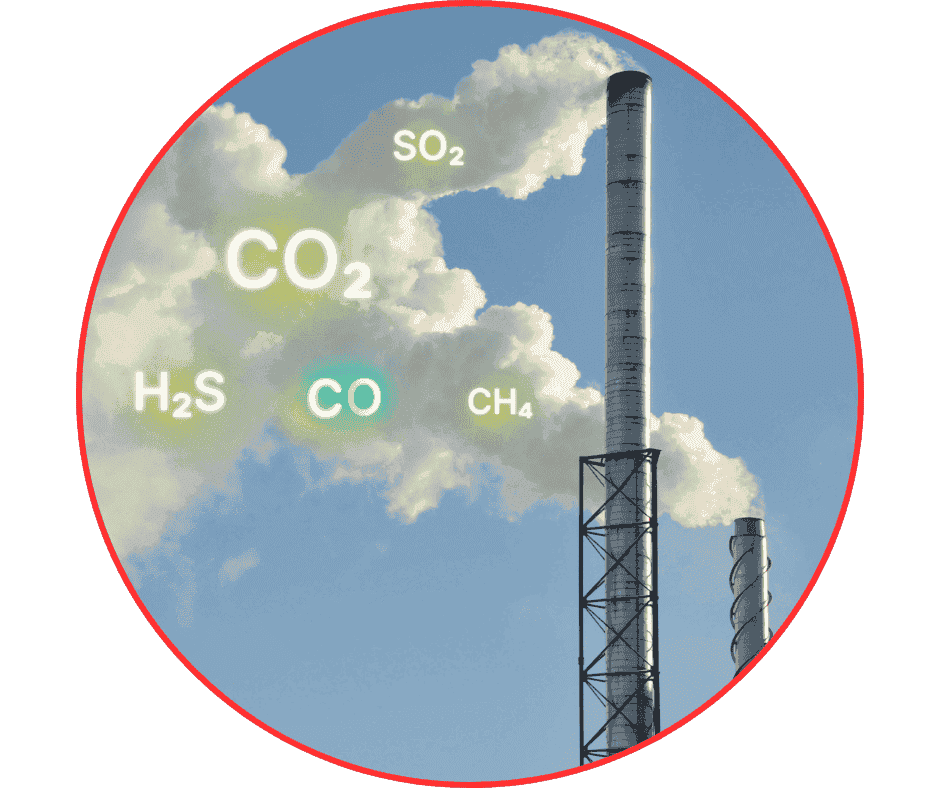 Harmful carbon monoxide (CO)
Harmful carbon monoxide (CO)Carbon monoxide (CO) is the most dangerous indicator in flue gas emissions. CO levels are mainly influenced by three factors:
-
Fuel moisture content
-
Combustion chamber temperature
-
Air-to-fuel ratio
In fixed grate boilers, manual fuel feeding often leads to fuel overload—especially when operators load too much wood at once.
This causes oxygen deficiency in the combustion chamber, generating high levels of harmful CO emissions and producing dense black smoke from the stack.
6. Steam Production Cost – Is the Fluidized Bed Boiler Truly More Cost-Effective Than the Fixed Grate Boiler?
Which boiler should you choose if your goal is to optimize steam production cost? This is a crucial question for manufacturers that consume large volumes of steam daily.
Key Components of Steam Production Cost
-
Fuel cost
-
Electricity, water, and chemical treatment cost
-
Labor and operation cost
Among these, fuel cost accounts for the largest proportion and directly impacts the cost per ton of steam produced.
The fluidized bed boiler achieves significantly higher combustion efficiency—over 85%, thanks to optimized air-fuel mixing and a dedicated combustion chamber.
As a result, fuel consumption per ton of steam is reduced by 15–20% compared to a fixed grate boiler.
Additionally, the fuel cost per kg is lower for fluidized bed boilers because they can burn low-cost small-sized biomass (such as rice husk, sawdust, cashew shell residue).
When combining fuel price and combustion efficiency, the fuel cost per ton of steam for fluidized bed boilers is typically 20–30% lower than that of fixed grate boilers.
7. Maintenance: Is the Fixed Grate Boiler Simpler While the Fluidized Bed Boiler Is More Complex?
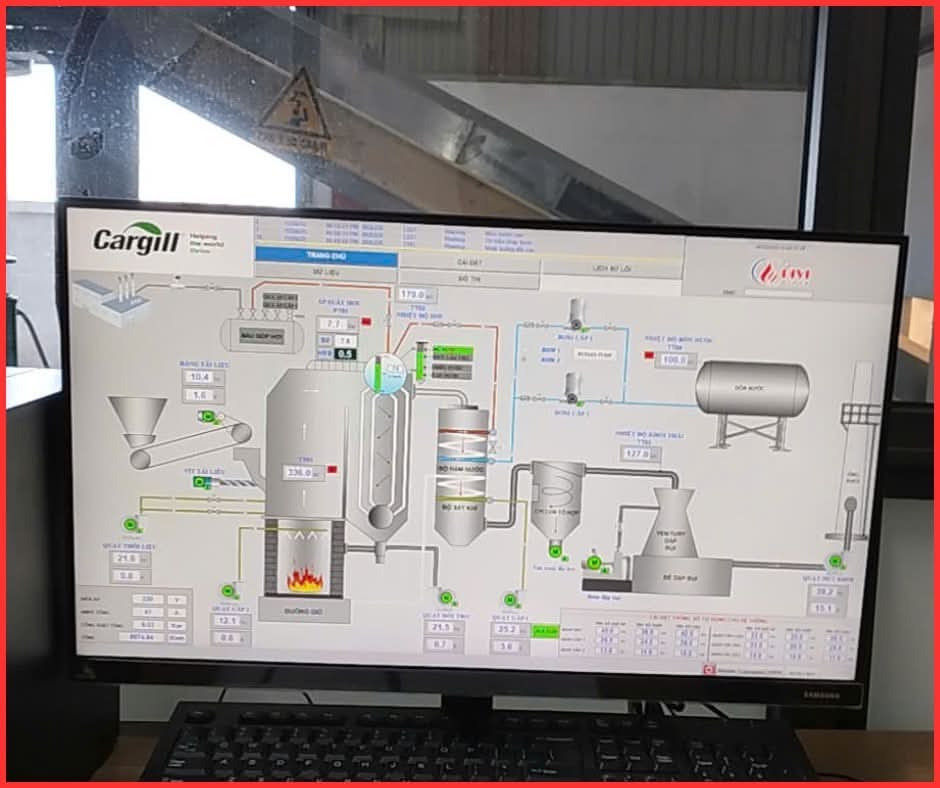 SCADA screen – equipment maintenance and servicing system
SCADA screen – equipment maintenance and servicing systemWhich boiler should you choose when it comes to ease of maintenance and servicing?
The fluidized bed boiler features a more complex structure, with many auxiliary systems such as the automatic fuel feeding system, fluidized air distribution grate, air preheater, and PLC–SCADA controls.
The fluidized bed boiler features a more complex structure, with many auxiliary systems such as the automatic fuel feeding system, fluidized air distribution grate, air preheater, and PLC–SCADA controls.
This makes maintenance quicker and easier. Even with a non-specialized team, businesses can keep the system running reliably as long as basic periodic checks are performed.
However, the simplicity of the fixed grate boiler comes at the cost of lower efficiency and a higher risk of operational issues, especially in production environments that demand stable performance and strict emission control.
8. Boiler lifespan: which boiler should you choose for long-term durability?
When designed to proper standards, combined with effective feed water treatment and regular blowdown, both fixed grate boilers and fluidized bed boilers can operate reliably for 10 to 20 years.
So if you are considering which boiler should you choose, rest assured that equipment lifespan is not the main deciding factor. What truly matters is whether the operation and maintenance procedures are performed correctly and consistently.
9. What is the ideal design capacity for each boiler type?
The fixed grate boiler is limited in capacity due to manual fuel feeding.
When capacity exceeds 5 tons/h, the amount of wood required per hour can reach 2.5 tons — beyond the ability of manual labor to handle efficiently. Frequent furnace door opening during fueling also causes combustion efficiency to drop significantly. In contrast, the fluidized bed boiler uses an automatic fuel feeding system, allowing it to handle larger capacities without affecting combustion performance.
However, if designed for very small capacities (below 2 tons/h), the investment cost may not be optimal. If you are deciding which boiler should you choose, base your choice on the actual steam demand.
- For small needs, a fixed grate boiler can be a temporary solution.
- For higher steam output and long-term goals, a fluidized bed boiler is the more sustainable and cost-effective choice.
Conclusion: which boiler should you choose for efficiency and fuel savings?
Fuel combustion efficiency is the key factor that impacts fuel consumption and operating cost. Technically, the fluidized bed boiler features a separate combustion chamber below the steam tubes.
This design allows combustion to occur first, followed by heat exchange, optimizing combustion intensity and ensuring near-complete fuel burn.
The fuel inside the fluidized bed furnace is suspended and thoroughly mixed with air, creating ideal combustion conditions. Air is supplied through small holes (about φ8mm), similar to the burner plate of a gas stove, producing a clean blue flame.
In comparison, the fixed grate boiler combines the combustion chamber with the steam tubes, causing interruptions in combustion.
The fuel often stays static, poorly mixed with air, leading to incomplete combustion and lower efficiency. The grate has large holes (30–50mm), which provide uneven air distribution and result in a red flame, similar to a gas stove without a burner plate.
Related Articles:
Additional Reference Videos:
8M kcal/h Biomass Thermal Oil Furnace – Cut Costs, Maximize Efficiency
Why This 5-Ton Fluidized Bed Boiler is a Game Changer for Factories
DIVI Group's Boiler Products:
Other news
-
Steam Separator – An Effective Solution for Dry Steam
29/12/2025, -
Treating High CO Emissions in Fixed-Grate Boilers – Is Boiler Replacement Necessary? Practical Solutions from DIVI
18/12/2025, -
What Is a Steam Trap? Principles, Types, and How to Select the Right Steam Trap for Your Steam System
07/12/2025, -
COMPARISON OF STEAM TRAPS: PRINCIPLES – EXPERIMENTS – OPTIMAL SELECTION FOR STEAM SYSTEMS
29/11/2025, -
Compact Biomass-Fired Boiler DVG-VN – The Optimal Fossil-Fuel Replacement Solution for Factories
23/11/2025, -
5 Common Mistakes in Industrial Steam Distribution Systems
11/06/2025, -
Mr. Boiler Speaks: Wake-Up Call from an Industrial Icon
09/06/2025, -
What is a Thermal Oil Heater? Structure, Benefits & Safety Tips
27/05/2025, -
3 Danger Signs of Boiler Operation You Should Never Ignore
24/05/2025, -
7 Common Causes of Boiler Flue Gas Issues – Effective Treatment Solutions
08/05/2025,

 EN
EN