What Is a Wood-Fired Boiler System?
Is your business seeking a cost-effective and eco-friendly energy source? A wood-fired boiler system might be the renewable solution you need. With rising fuel prices and growing environmental concerns, wood burning steam boilers offer efficient heat generation for various industries.
A wood fired boiler system is not only a cost-effective solution for fuel consumption but also a sustainable choice for environmental protection. By utilizing renewable biomass resources, this system contributes to reducing carbon emissions.
What Is a Wood-Fired Boiler System?
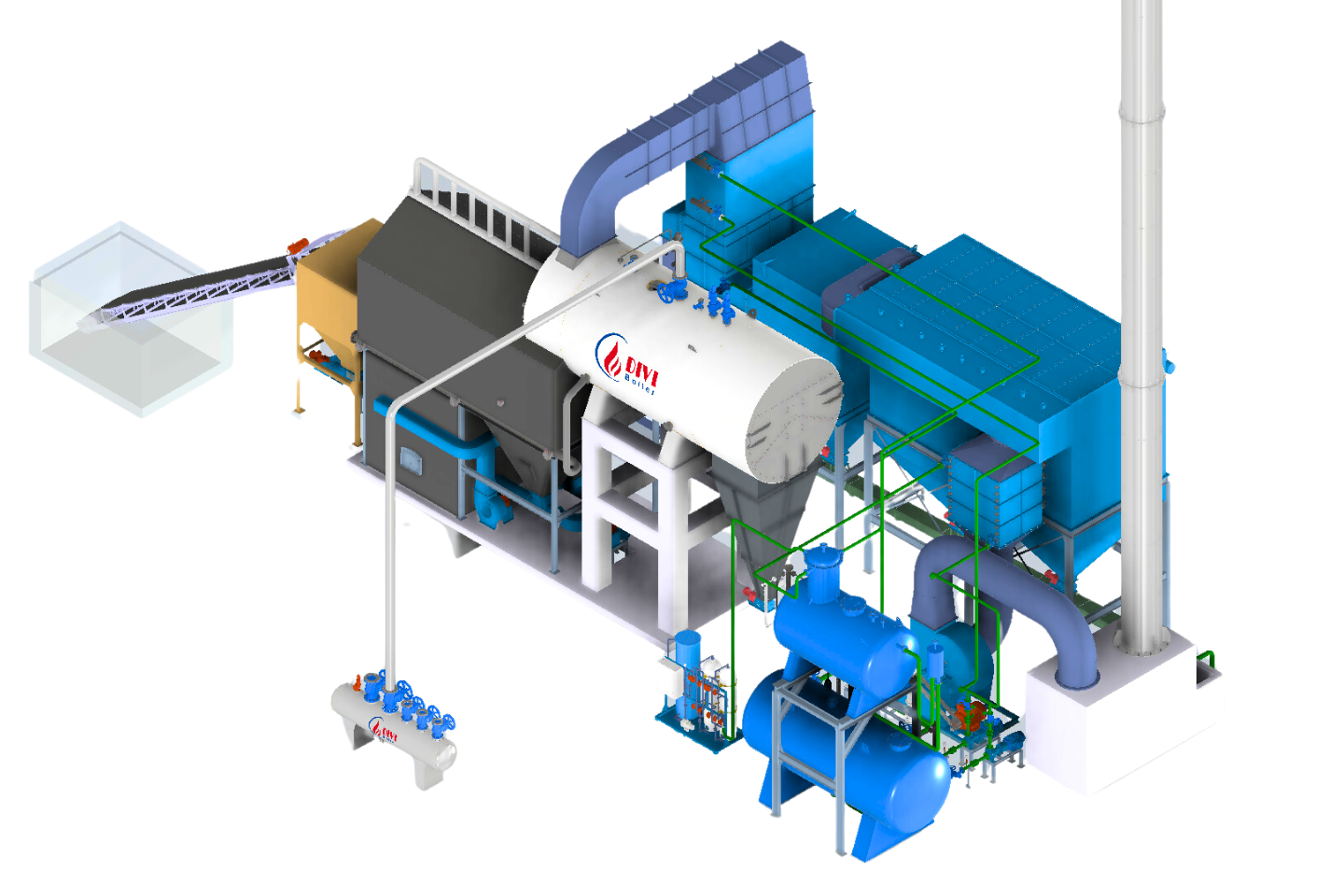
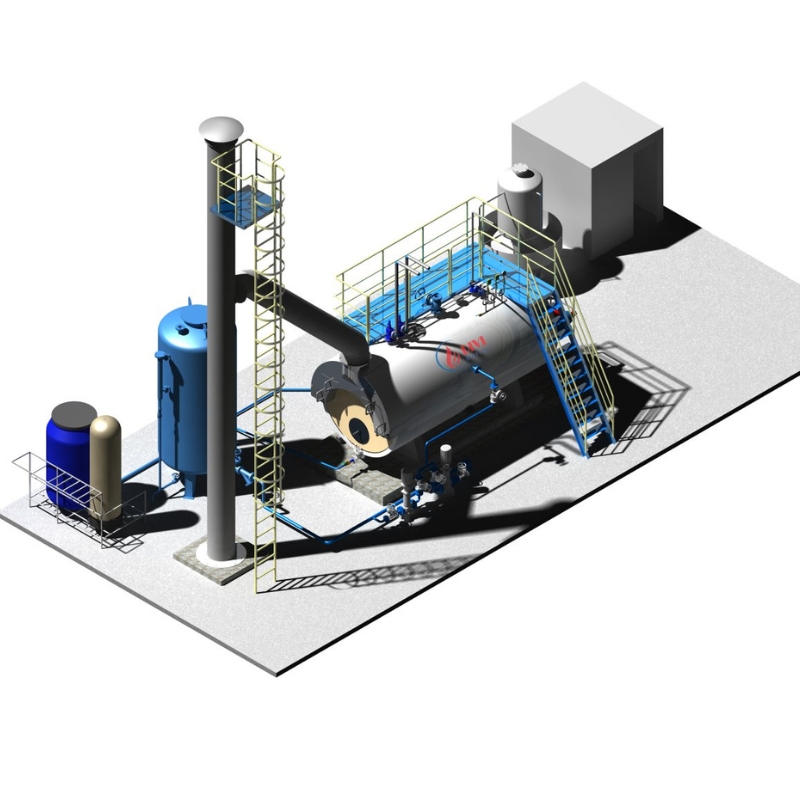
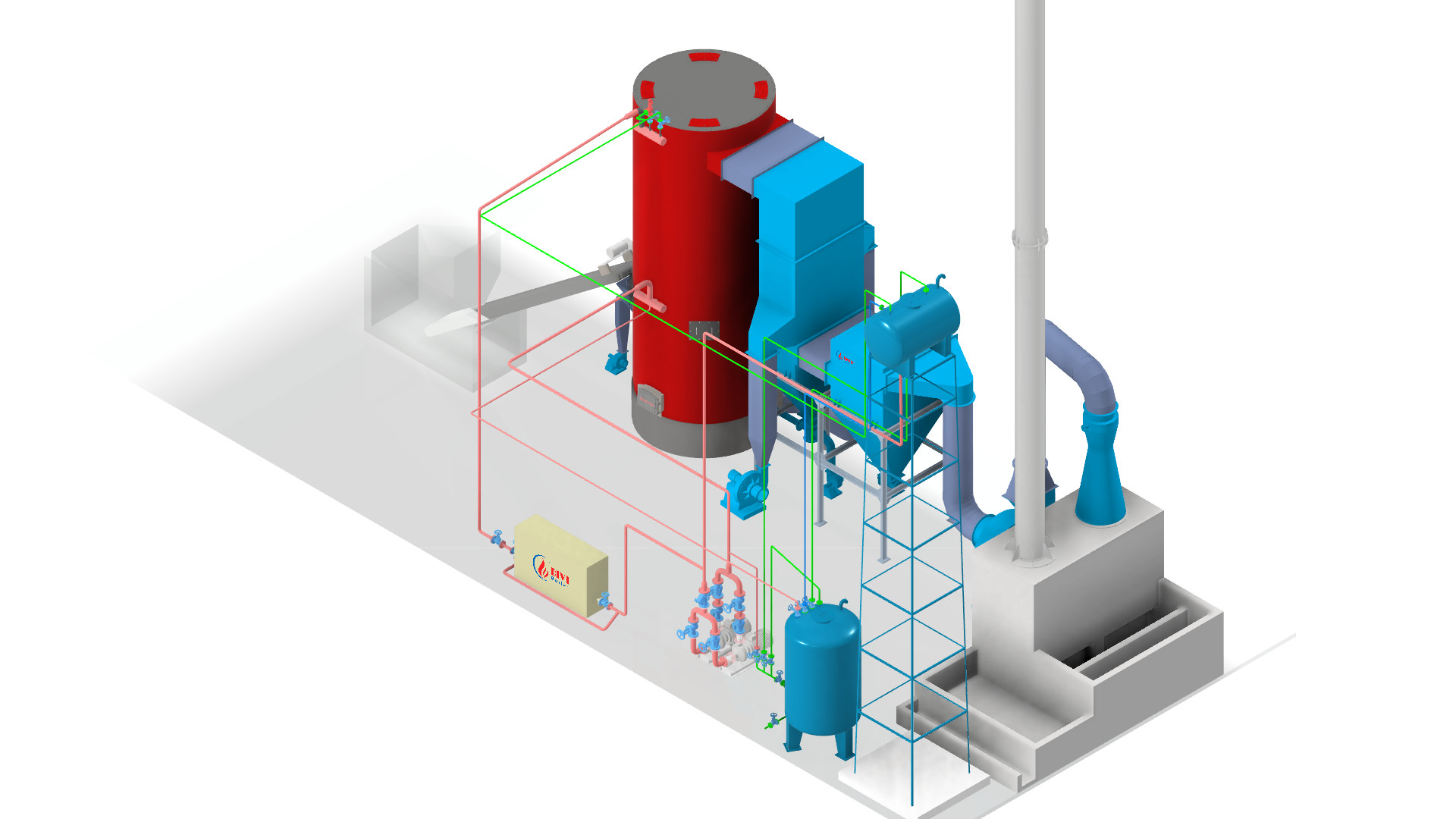
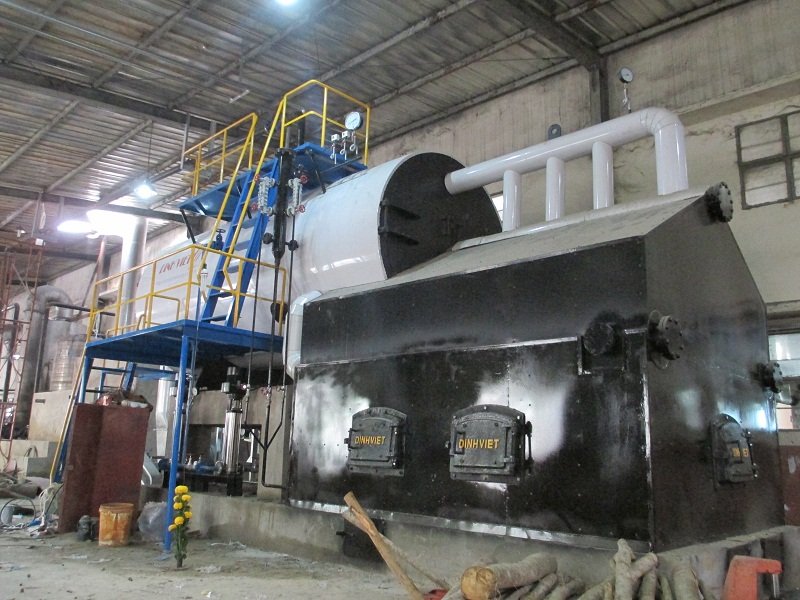
 Diagram of DIVI’s fixed grate wood-fired boiler system
Diagram of DIVI’s fixed grate wood-fired boiler systemA wood-fired boiler system—also called a wood burning steam boiler—is an industrial heating solution that utilizes biomass fuels such as firewood, sawdust, rice husks, and wood pellets to generate high-pressure steam. Unlike conventional fossil fuel systems, this setup leverages renewable energy sources, making it a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative for industrial operations.
Key Components of a Wood-Fired Boiler System:
- Combustion Chamber: Burns solid biomass fuel to produce thermal energy
- Heat Exchanger Tubes: Transfer heat from the combustion gases to water
- Steam Drum: Collects and stores pressurized steam for use
- Grate System (fixed or moving): Supports continuous fuel combustion and ash removal
These systems operate using natural or forced circulation, depending on capacity and design. They are also compatible with hybrid configurations like wood and oil fired boilers, offering flexibility in fuel selection and emission control.
How Does a Wood-Fired Boiler Work?
A wood fired boiler system operates through a simple yet efficient thermal process, designed to convert biomass fuel into usable industrial steam. Here's a breakdown of its working mechanism:
- Fuel Loading: Solid biomass like wood logs or pellets is fed into the combustion chamber.
- Ignition and Combustion: The fuel ignites, generating intense thermal energy.
- Heat Transfer: The generated heat passes through heat exchanger tubes, heating the surrounding water.
- Steam Generation: As temperature rises, water transforms into pressurized steam.
- Steam Delivery: The steam is directed to equipment or production lines that require consistent thermal output.
Compared to conventional oil or gas systems, wood and oil fired boilers share the same operational stages but differ significantly in fuel types and emission levels. While oil-based systems emit high levels of CO₂ and NOx, a wood burning steam boiler relies on renewable biomass, offering a more sustainable emission profile.

Advantages and Disadvantages of a Wood-Fired Boiler System
A wood fired boiler system provides a range of benefits, especially for industries seeking sustainable heat solutions. However, it also presents specific challenges that must be considered before installation.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Low operating costs compared to oil or gas | Limited capacity for large-scale, high-demand systems |
| Environmentally friendly due to renewable biomass fuels | Requires more installation space and storage area |
| Simple maintenance with fewer electronic components | Manual fuel feeding may reduce automation potential |
| Supports various biomass fuels (wood, husk, pellet, etc.) | Emissions require proper filtration to meet standards |
Expanded Benefits of Using a Wood-Fired Boiler
- Reduced carbon footprint due to CO₂-neutral combustion cycles, especially when biomass is sourced responsibly.
- Lower energy bills thanks to biomass fuel affordability, particularly in agricultural or rural areas.
- Flexible fuel options — many wood burning steam boilers can burn sawdust, rice husks, wood pellets, or even cashew shells, depending on availability.
- Simplified maintenance — the mechanical nature of these systems minimizes complex control failures.
Key Limitations to Consider
- Space requirements: Unlike compact oil systems, wood and oil fired boilers need space for fuel storage and manual loading zones.
- Labor-intensive feeding: Unless automated, biomass loading can be manual or semi-automated, requiring consistent supervision.
- Emissions management: If not equipped with filtration systems (e.g., ESP, bag filters), these systems may release PM, NOx, and CO, which can breach regulatory thresholds.
Popular Biomass Fuels for Wood-Fired Boiler Systems
 Wood pellet fuel used in the wood-fired boiler system
Wood pellet fuel used in the wood-fired boiler systemOne of the key advantages of a wood fired boiler system is its compatibility with various biomass fuel sources. Choosing the right fuel type is crucial for maintaining stable combustion, minimizing emissions, and optimizing energy efficiency.
- Wood pellets – Offer high heat density, low moisture, and are easy to transport and store. Ideal for automated feeding systems in wood burning steam boilers.
- Rice husks – Lightweight, inexpensive, and readily available in agricultural regions. Best for facilities with short production cycles.
- Bagasse (sugarcane waste) – A byproduct of sugar processing, commonly used in agro-industrial plants where supply is abundant and sustainable.
- Sawdust – Excellent for small-scale boilers or backup systems due to its fine particle size and quick ignition.
- Cashew shells – A form of recycled agricultural waste, widely used in regions with nut processing industries.
Each fuel type differs in calorific value, ash content, and combustion speed, so businesses should align fuel choice with operational needs, boiler capacity, and emission goals.
Common Industrial Applications of Wood-Fired Boiler Systems

A wood fired boiler system plays a vital role in many industries that require continuous and reliable steam generation. Its ability to operate with renewable fuels makes it ideal for businesses aiming to cut energy costs and reduce carbon emissions.
1. Food Processing Industry
Steam from a wood burning steam boiler is widely used in food production facilities for:
- Sterilization of packaging and equipment
- Boiling and cooking of raw materials
- Drying and pasteurization for product preservation
This sector values consistent steam output and precise temperature control, making biomass boilers a sustainable fit.
2. Textile and Garment Manufacturing
In textile plants, wood and oil fired boilers are utilized to:
- Perform pre-treatment (e.g., washing and scouring)
- Enable dyeing with uniform temperature control
- Support finishing processes like drying or shrinking fabrics
The hybrid fuel flexibility is useful where biomass is seasonal or limited.
3. Pulp and Paper Production
Paper manufacturing requires substantial thermal energy for:
- Drying large sheets of pulp
- Facilitating chemical pulping during cellulose breakdown
A wood fired boiler system ensures long-duration heat supply, aligning well with the high-energy demands of this industry.
Common Industrial Applications of Wood-Fired Boiler Systems
While there are various combustion methods used in a wood fired boiler system—including chain grate, fixed grate, and conventional fluidized bed combustion—two advanced technologies stand out for their adaptability and efficiency.
1. Reciprocating Grate Combustion Technology
This technology is ideal for wood burning steam boilers that must handle biomass fuels of inconsistent quality. It’s particularly effective when:
- Fuel has high moisture content
- Calorific value varies significantly
- Firewood comes in irregular shapes and sizes
The reciprocating grate operates in a stepped, rhythmic motion that enhances fuel agitation and air distribution, ensuring complete combustion even with low-grade or wet biomass. This makes it suitable for remote areas or industries using unprocessed or recycled biomass.
2. Circulating Fluidized Bed (CFB) Technology
Unlike traditional bed systems, CFB technology introduces a recirculation mechanism that allows precise control of combustion temperature. This is crucial when:
- Fuel characteristics change unpredictably
- Fine control is needed to prevent clinker formation
- Continuous operation is required under varying loads
Thanks to this adaptability, CFB systems ensure stable combustion, lower emissions, and improved thermal efficiency, even with challenging fuel inputs. For businesses that use hybrid fuels like in wood and oil fired boilers, CFB provides the flexibility to switch seamlessly between biomass and fossil fuels.
When Should You Use These Technologies?
- If your operation uses consistent, high-quality biomass, conventional grates or fixed bed systems may suffice.
- If you rely on diverse or unstable fuel sources, reciprocating grate or circulating fluidized bed technologies are the optimal choices.
FAQs – Wood-Fired Boiler Systems
1. What is a wood fired boiler system and how does it work?
A wood fired boiler system is a type of industrial steam generator that burns biomass fuels such as wood, sawdust, or rice husks to produce heat and steam. The process includes fuel combustion, heat transfer through exchanger tubes, and steam delivery to industrial equipment.
2. Are wood burning steam boilers environmentally friendly?
Yes. A wood burning steam boiler uses renewable fuels, making it more eco-friendly than oil or coal-based systems. It significantly reduces the carbon footprint when paired with proper emission control systems.
3. What are the fuel options for wood fired boilers?
Popular fuel types include wood pellets, rice husks, bagasse, sawdust, and cashew shells. Each fuel type affects combustion efficiency, heat output, and ash residue differently. Hybrid options like wood and oil fired boilers offer added flexibility in fuel selection.
4. How much space is required for installing a wood fired boiler?
A wood fired boiler system typically requires more installation space than a gas or oil boiler. This includes room for the combustion unit, fuel storage area, and ash handling system.
5. Is it possible to automate a wood burning steam boiler?
Yes. Many modern systems support semi- or fully-automated fuel feeding, ash removal, and airflow control. However, smaller units may still require manual loading depending on design and capacity.
Conclusion: Why Choose a Wood-Fired Boiler System?
If your business is looking for a cost-effective and eco-conscious heating solution, a wood fired boiler system offers a powerful combination of energy savings, operational reliability, and environmental compliance.
By selecting the right biomass fuel and applying modern technologies such as reciprocating grate or circulating fluidized bed combustion, your wood burning steam boiler can maintain stable thermal output even under fluctuating fuel conditions.
For facilities that require flexibility, wood and oil fired boilers allow seamless switching between biomass and fossil fuel, ensuring uninterrupted operation year-round.
Related Articles:
Additional Reference Videos:
8M kcal/h Biomass Thermal Oil Furnace – Cut Costs, Maximize Efficiency
How We Installed a 20T Biomass Fluidized Bed Boiler – Step-by-Step!
DIVI Group's Boiler Products:
Other news
-
Steam Separator – An Effective Solution for Dry Steam
29/12/2025, -
Treating High CO Emissions in Fixed-Grate Boilers – Is Boiler Replacement Necessary? Practical Solutions from DIVI
18/12/2025, -
What Is a Steam Trap? Principles, Types, and How to Select the Right Steam Trap for Your Steam System
07/12/2025, -
COMPARISON OF STEAM TRAPS: PRINCIPLES – EXPERIMENTS – OPTIMAL SELECTION FOR STEAM SYSTEMS
29/11/2025, -
Compact Biomass-Fired Boiler DVG-VN – The Optimal Fossil-Fuel Replacement Solution for Factories
23/11/2025, -
Which Boiler Should You Choose: Fixed Grate or Fluidized Bed? Detailed Efficiency, Cost & Environmental Comparison
24/06/2025, -
5 Common Mistakes in Industrial Steam Distribution Systems
11/06/2025, -
Mr. Boiler Speaks: Wake-Up Call from an Industrial Icon
09/06/2025, -
What is a Thermal Oil Heater? Structure, Benefits & Safety Tips
27/05/2025, -
3 Danger Signs of Boiler Operation You Should Never Ignore
24/05/2025,

 EN
EN