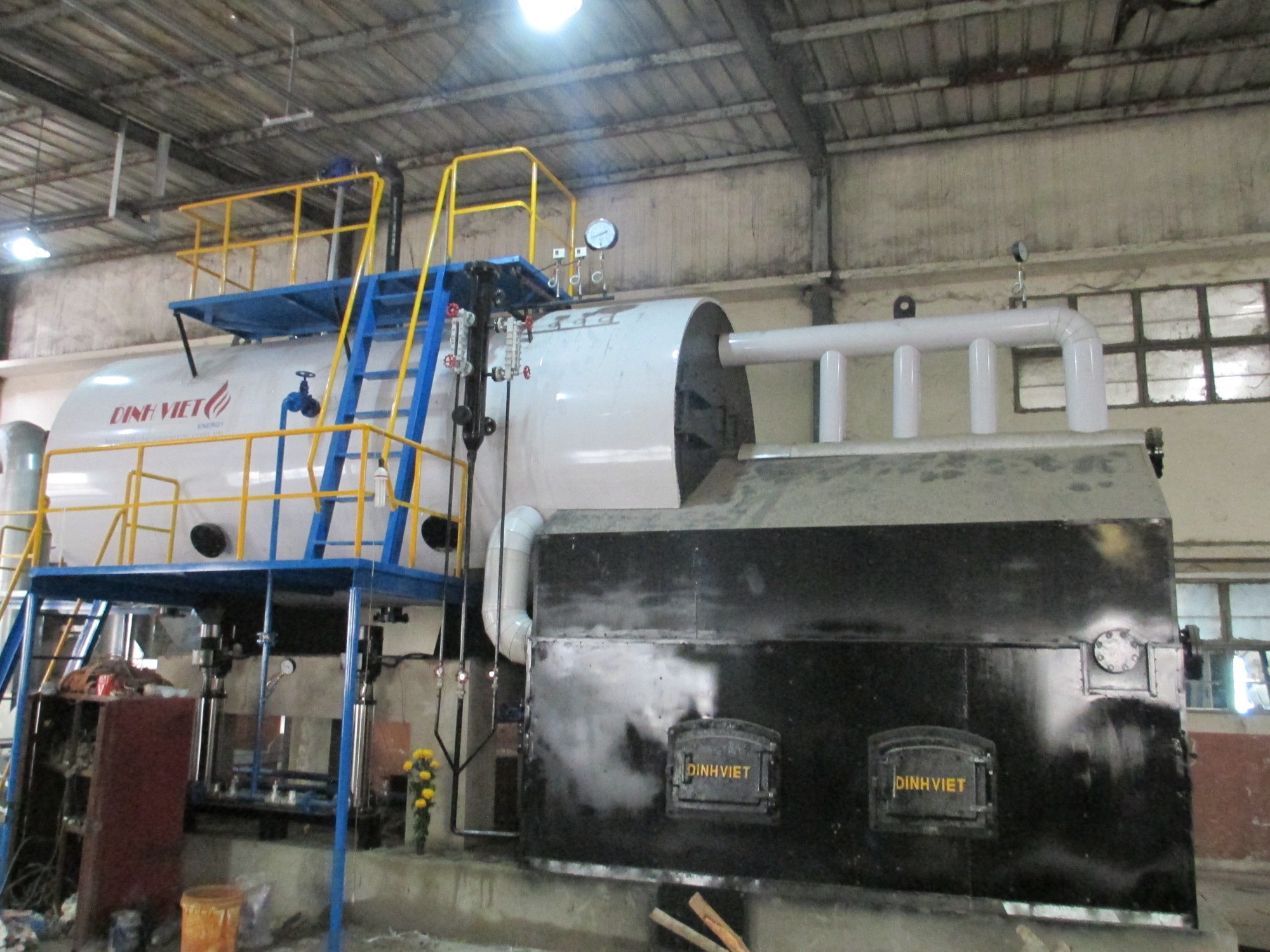
Top 5 Steps to Reduce Fuel Consumption for Boilers.
For businesses and industries that rely on boilers, fuel efficiency is a top priority. Whether you’re in manufacturing, food processing, or energy production, boiler fuel consumption directly impacts operating costs, environmental footprint, and overall profitability. Boiler fuel optimization not only reduces costs but also supports sustainable operations—a growing priority worldwide.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about boilers and boiler fuel, from boiler types and fuel choices to fuel-saving techniques, maintenance practices, and environmental considerations. By understanding and applying these principles, you’ll improve your boiler’s performance, reduce operational costs, and create a more sustainable business.
Understanding Boiler Types and Fuel Sources
Overview of Common Boiler Types
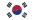
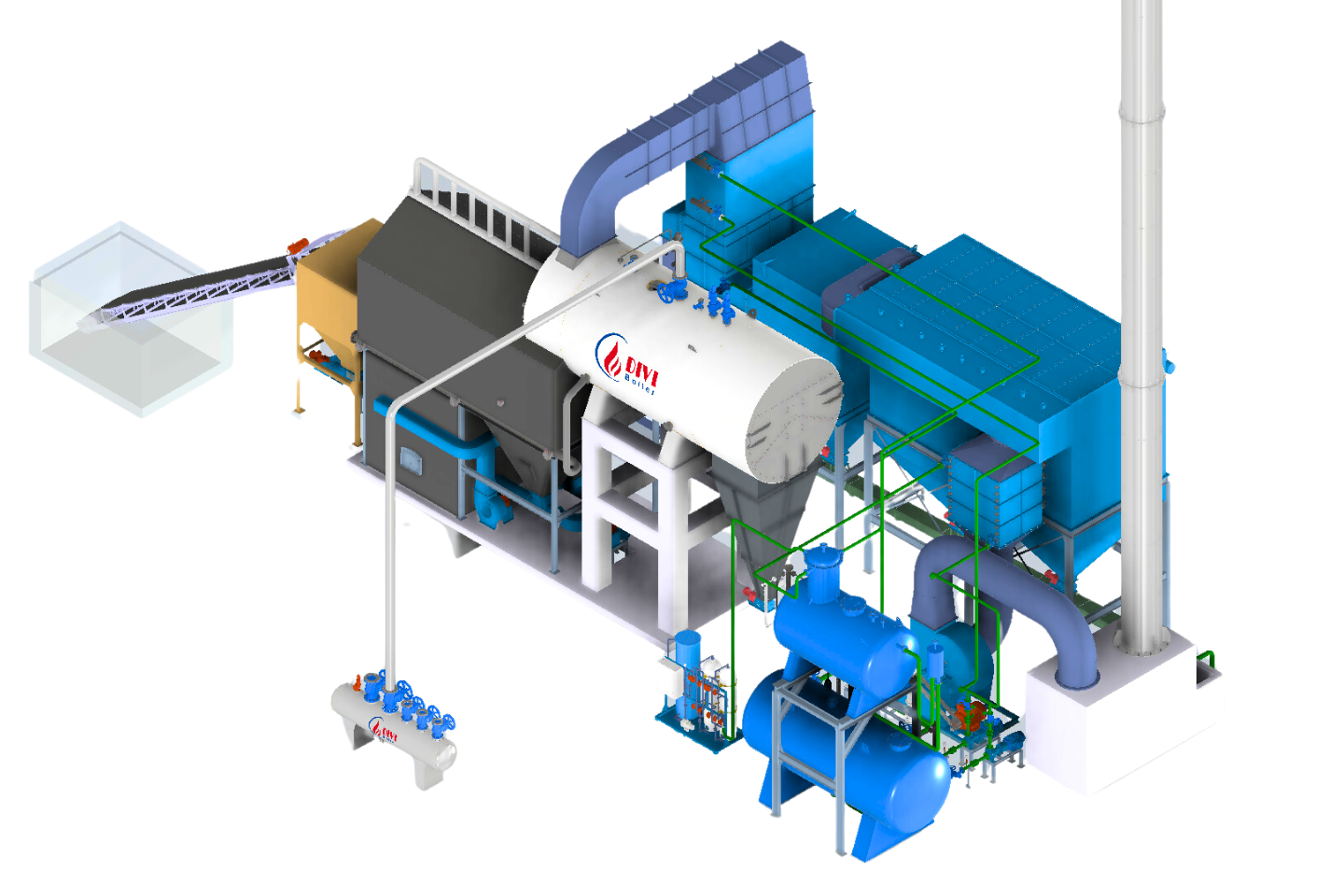
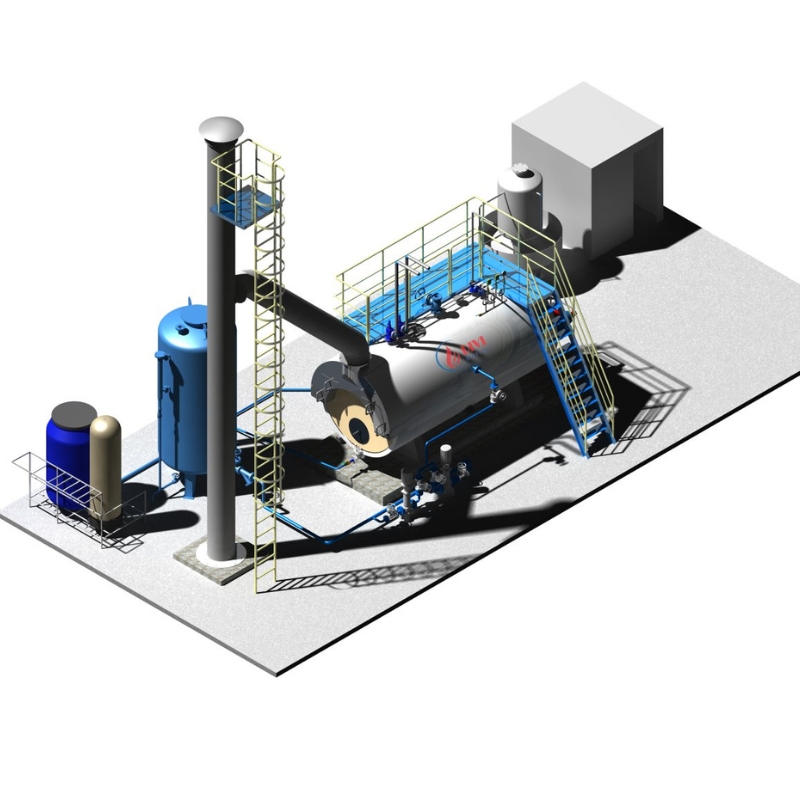
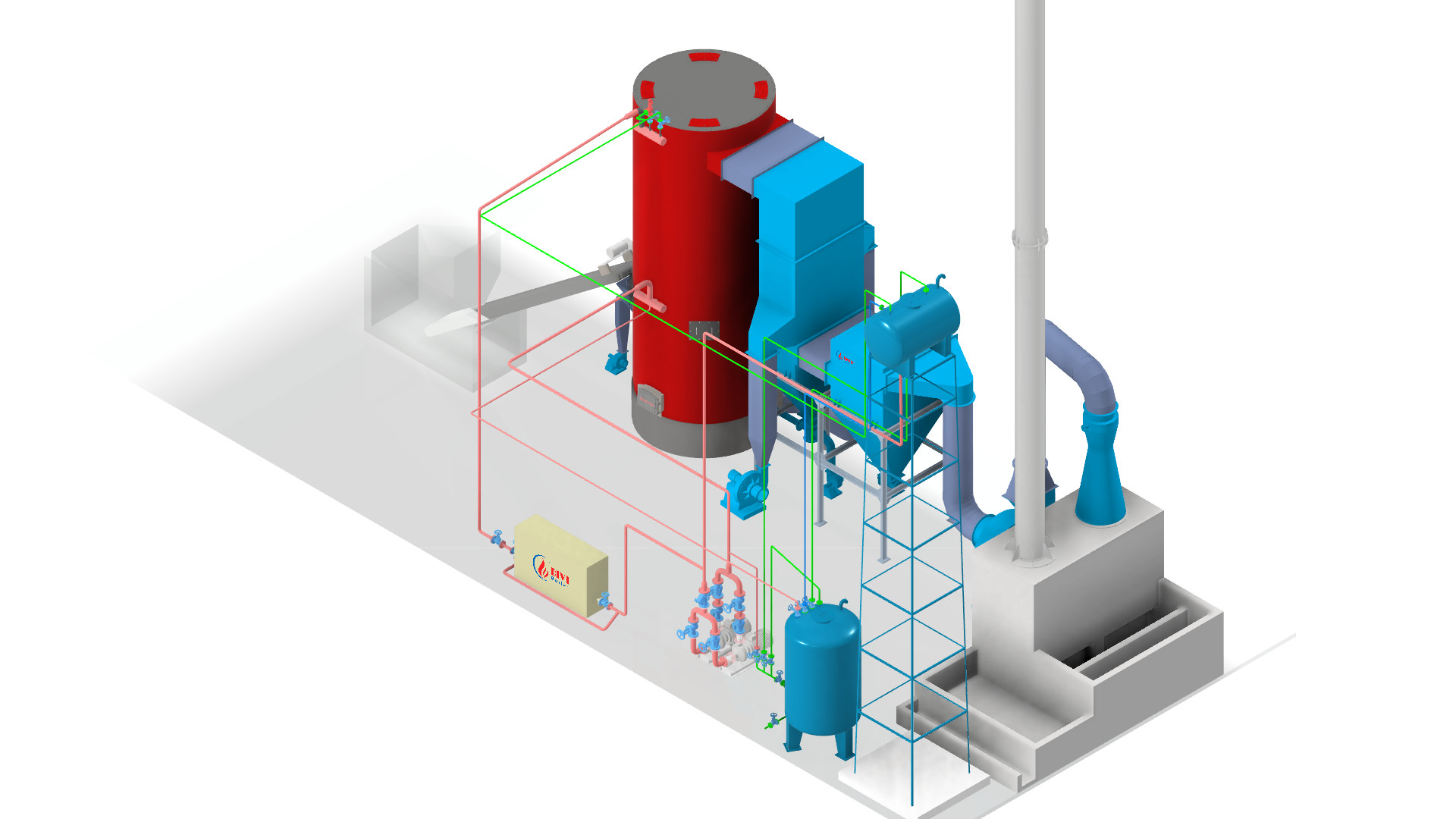
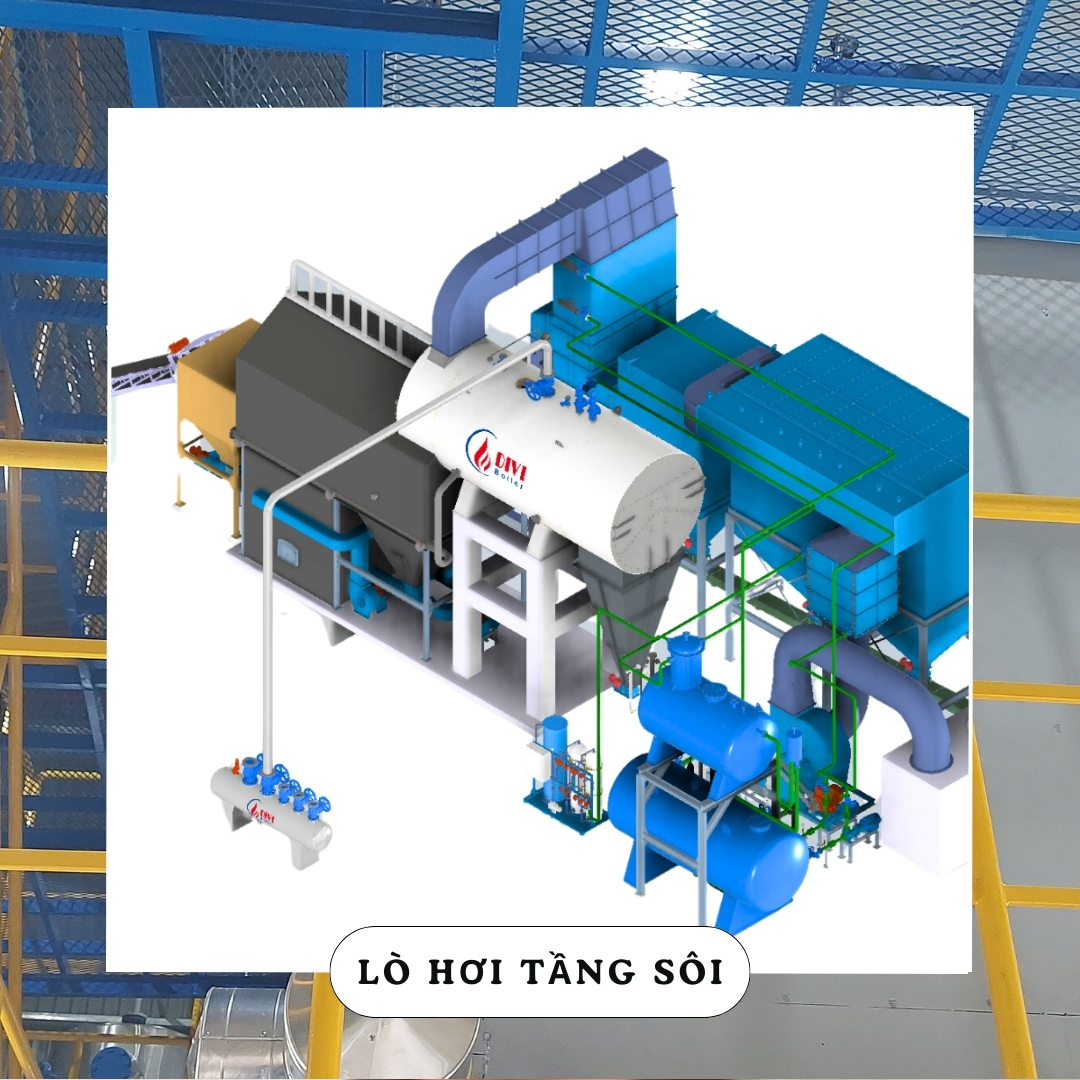
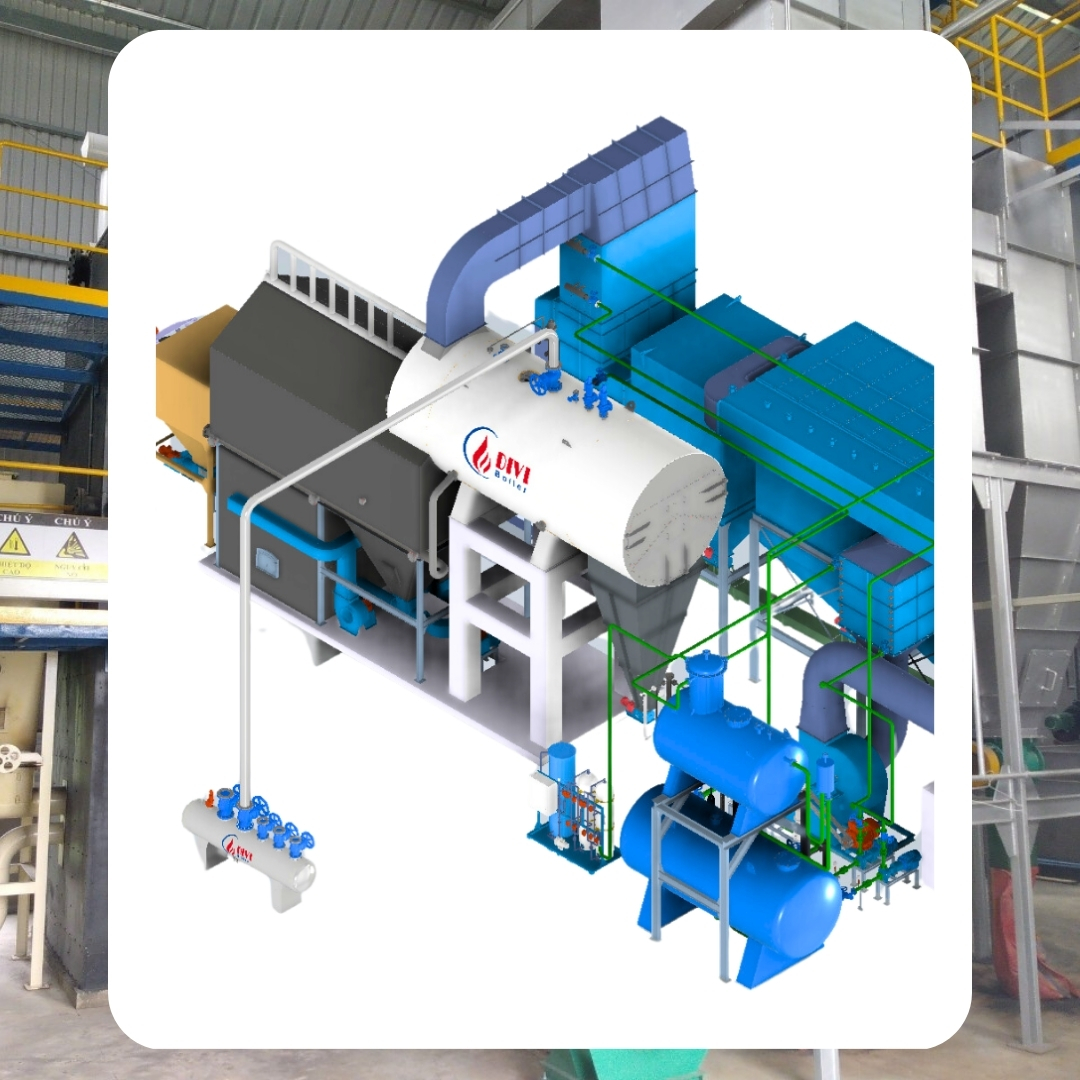 Divi Group fluidized bed boiler
Divi Group fluidized bed boilerBoilers come in several types, each with unique advantages, depending on the fuel source, application, and efficiency requirements:
- Fire-Tube Boilers: Ideal for lower pressure applications, fire-tube boilers heat water or steam through a series of tubes. Common in industrial and heating applications, they are generally more affordable but may consume more fuel.
- Water-Tube Boilers: These are suitable for high-pressure applications and industrial uses where high-temperature steam is needed. With water flowing through tubes heated externally, these boilers offer higher efficiency than fire-tube boilers but often come with a higher initial cost.
- Electric Boilers: A greener option for areas with high electricity availability, these boilers are energy-efficient and compact, ideal for small-scale applications.
- Condensing Boilers: Known for high efficiency, condensing boilers recover latent heat from exhaust gases, making them one of the most fuel-efficient options, especially for residential and commercial heating.
Common Fuel Sources for Boilers
The type of fuel you choose for your boiler will influence costs, efficiency, and environmental impact:
- Natural Gas: One of the most common boiler fuels due to its high energy density, relatively low cost, and cleaner emissions compared to coal or oil.
- Diesel and Oil: Often used in areas without natural gas access, diesel is efficient but may involve higher emissions and fuel costs.
- Biomass: This renewable source includes wood pellets, agricultural waste, and other organic materials. It’s more sustainable but may require specific boilers and produce variable efficiency.
- Electricity: Best for areas with abundant power sources, electric boilers have zero direct emissions but can be costly if electricity rates are high.
Selecting the best fuel depends on availability, cost-effectiveness, and your boiler’s specifications.
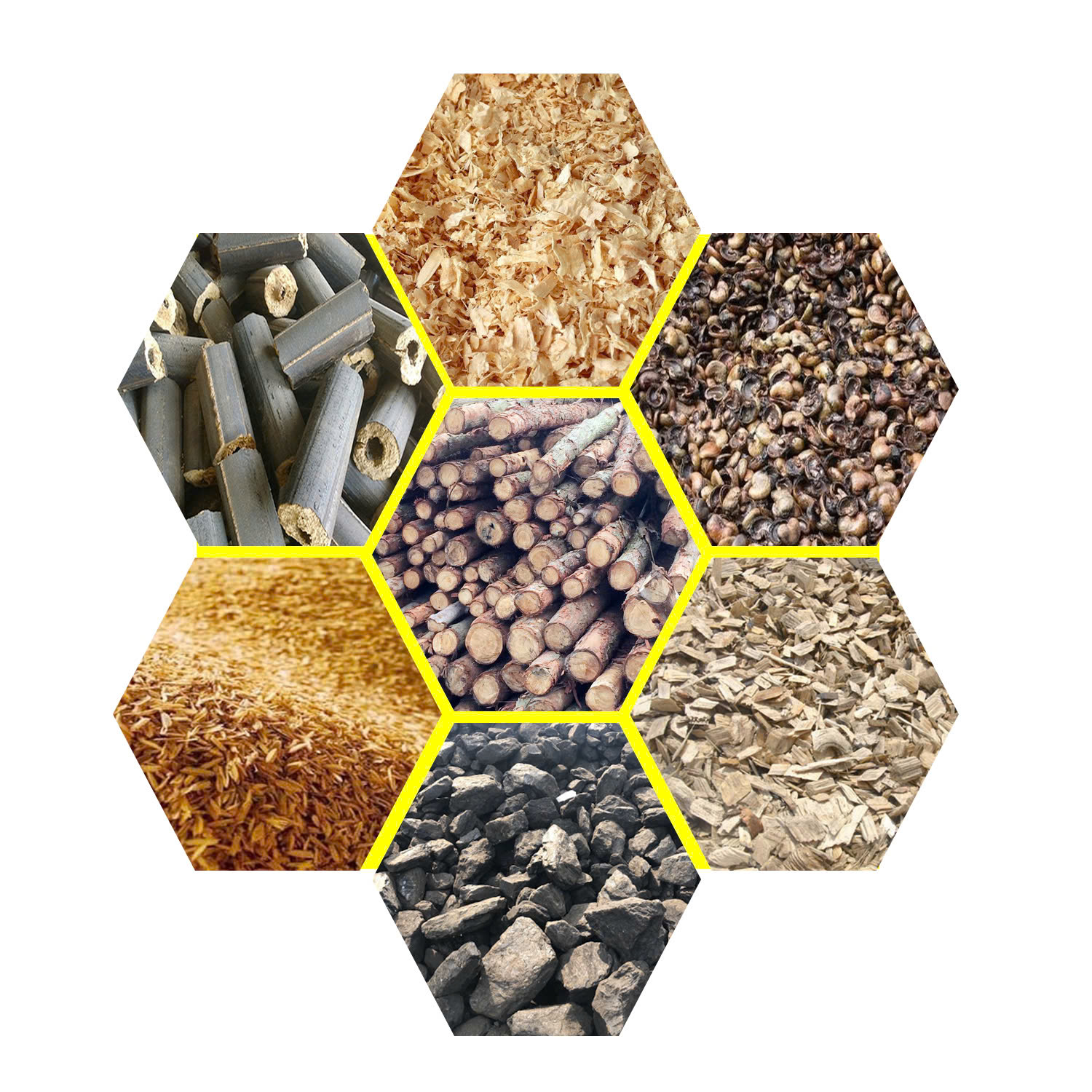 Common Fuel Sources for Boilers
Common Fuel Sources for Boilers Factors Influencing Boiler Fuel Consumption
Fuel consumption in boilers is affected by multiple factors, including boiler type, fuel quality, and operational practices. Understanding these factors can help you make informed adjustments to reduce fuel use.
- Boiler Size and Load: Larger boilers, or those under heavier loads, naturally consume more fuel. Balancing boiler capacity with demand can reduce fuel waste.
- Fuel Quality: High-quality fuels with low moisture content burn more efficiently, reducing fuel consumption.
- Maintenance Practices: Regular cleaning and preventive maintenance keep boilers running efficiently, reducing fuel wastage.
- Operational Efficiency: Proper adjustment of fuel supply, air intake, and combustion rates all help optimize fuel use.
5 Essential Steps to Reduce Fuel Consumption
Step 1: Regular Boiler Cleaning and Maintenance
 Regular Boiler Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular Boiler Cleaning and MaintenanceKeeping the boiler clean is crucial for maintaining optimal heat transfer. Over time, soot and scale buildup can reduce efficiency by obstructing heat transfer surfaces.
- Weekly Cleaning: For boilers running daily, a weekly internal and external cleaning helps maintain performance.
- Component Inspection: Regularly inspect burners, tubes, and exhaust systems for signs of fouling or corrosion.
- Heat Transfer Efficiency: Clean boilers transfer heat better, which improves fuel efficiency and reduces costs.
Step 2: Control Moisture Content in Fuel
Fuel moisture can significantly impact combustion efficiency. High moisture in biomass, wood pellets, or other fuels can increase fuel consumption and reduce efficiency.
- Storage Practices: Ensure fuel storage areas are dry and protected from rain or snow.
- Fuel Quality Monitoring: Regularly test moisture content and choose suppliers who provide dry, quality fuel.
- Efficiency Gains: Low-moisture fuels burn hotter and more efficiently, which can save up to 10-20% in fuel costs.
 Control Moisture Content in Fuel
Control Moisture Content in FuelStep 3: Adjust Fuel Supply for Optimal Combustion
 Adjust Fuel Supply for Optimal Combustion
Adjust Fuel Supply for Optimal CombustionFor efficient boiler operation, fuel should be supplied in measured amounts. Overloading the combustion chamber can lead to incomplete combustion and higher fuel consumption.
- Automated Controls: For advanced systems, set automated controls to regulate fuel feed based on steam demand.
- Manual Feeding Techniques: In manual systems, train operators to add fuel in small, consistent amounts to maintain steady combustion.
- Continuous Operation: Adjusting fuel supply to match operational needs helps maintain consistent combustion and prevents excess fuel use.
Step 4: Optimize Air and Oxygen Levels
 Optimize Air and Oxygen Levels
Optimize Air and Oxygen LevelsEffective combustion requires a balance of fuel and oxygen. Too much or too little air supply can reduce efficiency and increase fuel consumption.
- Airflow Adjustment: Monitor airflow based on the fuel input rate to ensure complete combustion.
- CO Monitoring: Using a CO meter can help identify incomplete combustion, indicating the need for adjustments.
- Efficient Combustion: Ideal air-fuel ratios minimize fuel wastage, ensuring more complete fuel combustion.
Step 5: Regular Blowdown and Scale Control
Boiler scale buildup can drastically reduce heat transfer efficiency, leading to higher fuel consumption. Performing routine blowdown and water treatment prevents scale accumulation.
- Routine Blowdown: Conduct blowdown at least once per shift to remove impurities from boiler water.
- Chemical Treatments: Use appropriate chemicals to prevent scale and corrosion, which can lower fuel efficiency by up to 20%.
- Long-Term Savings: Regular maintenance saves fuel costs and extends the lifespan of the boiler.
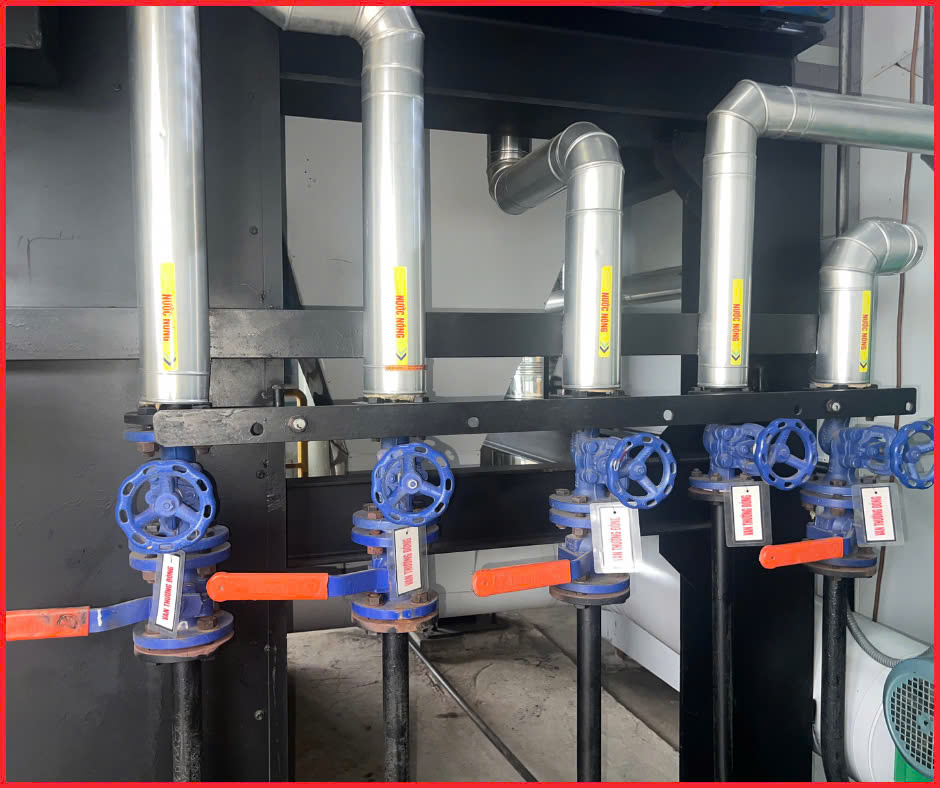 Regular Blowdow
Regular BlowdowAdvanced Boiler Fuel-Saving Techniques
 Advanced Boiler Fuel Saving Techniques
Advanced Boiler Fuel Saving Techniques
Using CO Meters for Combustion Optimization
A CO meter is an invaluable tool for optimizing combustion. By measuring CO levels in exhaust gases, operators can adjust air and fuel input for better efficiency.
- CO Levels: Low CO levels indicate efficient combustion, reducing unburned fuel and maximizing heat transfer.
- Investment Worth: Though it requires upfront costs, a CO meter can provide long-term fuel savings and efficiency gains.
Insulating Boiler Components
Insulating pipes, boiler walls, and other components minimizes heat loss, especially in colder climates or uninsulated facilities.
- Heat Retention: Insulation keeps heat within the boiler, reducing the fuel needed to maintain temperature.
- Return on Investment: Insulation upgrades pay off in fuel savings and reduced energy costs.
Automated Control Systems for Fuel Management
Modern boilers often come with advanced control systems that adjust fuel and air based on demand and efficiency requirements.
- Automated Adjustment: Systems can regulate fuel and oxygen input, ensuring ideal combustion at all times.
- Efficiency Boost: Automation minimizes human error, maintaining consistent fuel usage and improving overall efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Boiler Fuel Emissions
 Environmental Impact and Boiler Fuel Emissions
Environmental Impact and Boiler Fuel Emissions Reducing emissions is both an environmental and regulatory priority. Key pollutants from boiler fuel combustion include CO2, NOx, and particulate matter.
- Emission Control Devices: Use scrubbers, filters, or other equipment to reduce pollutant release.
- Cleaner Fuel Options: Switching to cleaner fuels like natural gas or biomass can lower emissions significantly.
- Environmental Compliance: Regularly monitor emissions to comply with local environmental regulations.
Optimizing Boiler Fuel Use for Sustainable Operations
Incorporating sustainable fuel practices can reduce environmental impact and improve long-term costs. Here’s how:
- Biofuels and Biomass: Transitioning to renewable fuels reduces dependence on fossil fuels and cuts carbon emissions.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining renewable energy sources with traditional fuels can improve cost efficiency while lowering emissions.
- Regulatory Benefits: Many governments offer incentives for sustainable practices, reducing the financial burden of initial investments.
Conclusion
Optimizing boiler fuel efficiency is critical for cost savings, environmental sustainability, and operational success. By implementing these techniques, you can significantly reduce fuel consumption, lower emissions, and enhance your boiler’s performance. Start with the basic steps, and then incorporate advanced techniques to maximize efficiency. Remember to monitor improvements and make adjustments as needed.
Additional Reference Videos:
[DIVI] What Is The Boiler
[DIVI] 2 Simple Steps For Operating A Boiler Safely
DIVI Group's Boiler Products:
Other news
-
Steam Separator – An Effective Solution for Dry Steam
29/12/2025, -
Treating High CO Emissions in Fixed-Grate Boilers – Is Boiler Replacement Necessary? Practical Solutions from DIVI
18/12/2025, -
What Is a Steam Trap? Principles, Types, and How to Select the Right Steam Trap for Your Steam System
07/12/2025, -
COMPARISON OF STEAM TRAPS: PRINCIPLES – EXPERIMENTS – OPTIMAL SELECTION FOR STEAM SYSTEMS
29/11/2025, -
Compact Biomass-Fired Boiler DVG-VN – The Optimal Fossil-Fuel Replacement Solution for Factories
23/11/2025, -
Which Boiler Should You Choose: Fixed Grate or Fluidized Bed? Detailed Efficiency, Cost & Environmental Comparison
24/06/2025, -
5 Common Mistakes in Industrial Steam Distribution Systems
11/06/2025, -
Mr. Boiler Speaks: Wake-Up Call from an Industrial Icon
09/06/2025, -
What is a Thermal Oil Heater? Structure, Benefits & Safety Tips
27/05/2025, -
3 Danger Signs of Boiler Operation You Should Never Ignore
24/05/2025,

 EN
EN